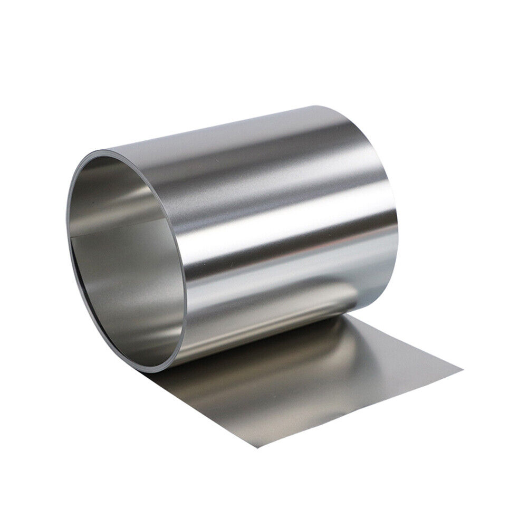
Both residential and commercial buildings have increasingly relied on galvanized metal sheeting for rust-proof and long-lasting roofing. This guide focuses on the materials, nature, pros, and uses of galvanized metal. This article makes sure the reader understands everything from the galvanization process and its durability to the different designs and climates it accommodates. In this guide, homeowners looking for affordable yet reliable roofing and builders in need of economical materials are both covered.
What is galvanized metal sheeting and how is it made?

Galvanized metal Sheeting consists of steel and iron, which are covered with a protective layer of zinc in order to avoid corrosion and rust. This is done through a process called galvanization wherein the metal is either dipped into molten zinc (which is referred to as hot dip galvanizing) or electrochemically coated (which is called electro-galvanizing). Galvanized metals can be used in construction, roofing, and several other outdoor applications, as they are very durable and have an extended lifespan owing to the zinc layer which acts as a protective barrier.
Understanding the galvanization process
embracing the galvanization process is paramount in ensuring the longevity and performance of metal products. Galvanization involves the formation of a protective zinc coat that not only protects the metal underneath from the surrounding elements but also provides a catalytic shield. This protective method ensures that in the scenarios where the zinc covering is scratched, the corrosion that occurs will mainly eat into the zinc and not the metal that is underneath. Depending on the application required and desired thickness of the zinc layer, the hot-dip method and electro-galvanizing method may be used and this decision is often subjective. Both methods provide advantages, pero exact specification of your desires will prompt you to make the appropriate decision.
Hot-dip galvanizing vs. other methods
Like with or unlike other methods, the fundamental difference when comparing hot-dip galvanizing to other systems stems from its durability and application requirements. The famed hot-dip galvanizing method uses a Zn coating which is more durable and resistant to corrosion for a more extended time period in harsher environments. Other methods, for example electro-galvanizing, apply Zn coating that is thinner and accommodating for applications requiring more precision and smoother finishes. It all vents down to the degree or priority of functional or aesthetic goals and their environmental demands.
The role of zinc coating in corrosion resistance
it is evident that zinc coating increases the lifespan of metal structures because of its unmatched corrosion resistance. I have personally witnessed how zinc establishes a protective barrier that not only provides direct shielding to the metal against corrosive elements, but also offers anodic protection. This means that even when the coating suffers damage, the zinc does not stop corroding. Rather, it preferentially dissolves, ensuring its base material is protected. Choosing the appropriate zinc coating procedure, be it hot-dip galvanizing or electro-galvanizing, has a huge impact. Each process has its own advantages, and optimizing for particular environmental conditions and usage requirements needs to be done to ensure performance over extended periods.
What are the benefits of using galvanized steel sheets?

The protective zinc layer guarantees prolonged efficiency in unfavorable surroundings while minimizing the chances of deterioration and rust damage. They are also greatly strong for their low weight, can be used in commercial, residential, and industrial environments, and can be recycled, further helping the environment. That, in combination with weak maintenance and versatility makes galvanized steel sheets cost-effective for a range of purposes. Furthermore, their use not only meets but also contributes towards setting environmental standards.
Superior corrosion resistance and durability
I know from experience that having good corrosion resistance is crucial for the trusted durability of many structures and components. Materials that have been galvanized are preferable over other materials due to their better performance in hostile conditions where water, harmful chemicals, and other corrosive substances are present. Their longevity reduces maintenance expenditures over extended periods, giving a sense of assurance for projects needing structural integrity over time.
Cost-effectiveness and longevity
As a result of their ability to emerge essentially unscathed from harsh external forces, galvanized materials are famously cheap and last a long time. Such materials guarantee structural integrity for decades and aid in providing a lower total cost of ownership, since repairs and replacements are not required frequently. These facets, in combination, make such materials ideal for projects requiring seamless durable and economic solutions.
Versatility in various applications
I have seen how galvanized materials perform superbly in various industries. Their versatility is unmatched in construction, automotive production, or even agricultural infrastructure. To illustrate, galvanized steel is used extensively for construction of bridges, as well as for fences and pipes, because of its durability and resistance to corrosion. Its versatility stems from its capability to operate effectively under extreme conditions, which makes it an invaluable tool in industries that need dependability and efficiency.
How does galvanized metal sheeting compare to other roofing materials?
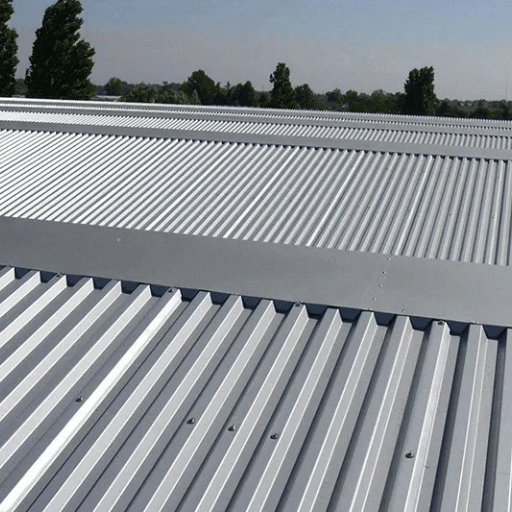

Galvanized metal sheeting is one of the best options concerning roofing materials, as it is both incredibly durable and cost effective. Unlike other materials like wood or asphalt shingles, galvanized metal does not corrode or weather over time, directly increasing its lifespan, even in awful climates. On top of that, its low weight increases ease of installation and reduces structural stress. Unlike other materials, galvanized metal reflects sunlight greatly, which increases energy efficiency. Overall, these characteristics make galvanized metal a useful and dependable material for both residential and commercial use.
Galvanized steel vs. traditional roofing options
Galvanized steel clearly comes out on top against asphalt shingles and wood. It has several advantages over them. Here are some of the key factors one should keep in mind:
- Durability – The Steel’s zinc galvanization offers protection from rust like corrosion. This protective form enables it to weather heavy storms, rains and a lot of sunlight much better than wood which tends to rot or asphalt shingles which can deteriorate over an extended period of time.
- Longevity – A steel roof has a lifespan of 40-70 years unlike asphalt shingles which have a lifespan of 15-30 years. Having fewer replacements and less headaches over time due to a longer lifespan is quite a beneficial economic investment.
- Weight – Galvanized steel roofs have a lot lower weight in comparison to traditional roofing materials which makes installation a lot convenient as well as reduces the Load on the structure which is highly beneficial to older buildings or homes that lack proper structural support.
- Energy Efficiency – Steel is also really good at reflecting sunlight. For galvanized steel roofs, their reflective properties enable cooling of the roof temperature, thus lowering the cooling costs during summer. Asphalt on the other hand, tends to trap heat.
- Maintenance – Galvanized steel roofs do not need much maintenance, unlike wood that has to be treated for pests and rotting, or asphalt shingles that need sections replaced periodically. Their toughness means less repairs and minimal upkeep overall.
In summary, although conventional roofing materials may seem easier or cheaper at first, galvanized steel outmatches them when considering durability, energy efficiency, and maintenance in the long run. Anyone searching for an effective and dependable roofing material should choose it without doubt.
Environmental impact and sustainability
Galvanized steel roofing is an environmentally sustainable option because it is highly recyclable and lasts a long time, minimizing frequent replacements and material waste. Additionally, its energy-efficient reflective properties reduce heat absorption which diminishes cooling needs. Therefore, it is a sustainable roofing option for construction purposes.
Aesthetic considerations for metal roofing
Often, I point out the flexibility and customization capabilities that come with an aesthetic consideration for metal roofing. Metal roofing can come in different styles, colors, and finishes, giving homeowners or builders the opportunity to accompany any architectural design. If the goal is a straightforward, modern look, standing seam panels are sleek; if a more traditional look is preferred, there are textured finishes that resemble wood and slate. In addition to these options improving aesthetics, they are also practical in terms of enhancing curb appeal while not sacrificing durability or performance, which is critical.
What are the common applications for galvanized steel sheets?

The use of galvanized steel sheets spans multiple sectors due to their high strength and unparalleled resistance to corrosion. These sheets have become exceedingly common in modern construction for roofing and siding, automotive industry for body panels, as well as HVAC ducting and electrical cabinets fabrication. They also have a wide use in agricultural for fencing, silos and storage tanks, along with their incorporation into home appliances such as refrigerators and washing machines. Because of their strength and versatility, galvanized steel sheets can be employed in useful and aesthetic applications.
Roofing and construction uses
that utilizing galvanized steel for roofing and other construction activities has always been a safe bet. The material is exceptionally durable and can withstand rust, which makes it perfect for extreme weather conditions. In my previous projects, it has been utilized as roofing sheets, structural beams, and gutters where its anti-corrosive attributes prolong the life of the components. It also possesses other advantages such as offering a good strength to weight ratio which aids in effortless handling and installation as compared to some other materials. Galvanized steel is a go-to material for new constructions and also for renovations because it offers value for money and performs remarkably well.
Automotive and industrial applications
Due to its strength and anti-corrosive qualities, galvanized steel is popular in the automotive and industrial sectors. In the construction of automobiles, it is used for car bodies, frames, and undercarriages to prevent rusting from moisture and road salt. In industrial applications, it is also preferred for reliable and strong machinery, pipelines, and storage tanks. Its low cost, along with relatively inexpensive maintenance, further affirm its value in these industries.
Agricultural and residential implementations
Supplemental fences, storage silos, and farming equipment are examples in which agriculture relies on fences in harsh environmental conditions. In residential settings, these materials also find their place in roofing, gutters, and structural reinforcements. Both implementations, agricultural and residential, strive to optimally balance cost, durability and reliability to cater to the particular needs of the structure and its use. My personal view is that material selection is not only about achieving desired outcomes, but creating value in the long term.
How to properly maintain and care for galvanized metal sheeting?

In order to maintain galvanized metal sheeting, proper maintenance and care involve some steps which are essential for its longevity and performance. Use gentle soap and water on the surface in order to remove any pollutants that have the possibility of speeding up corrosion. Do not use tools or cleaners that are abrasive as they may scrub off the protective zinc coating. Look for scratches or other exposed areas periodically, and if you find any, cover those with protective products like zinc rich paint, which acts as a rusting preventative. Metal moisture build up can be reduced by drying the metal and ensuring it is well ventilated. Their integrity can also be maintained by avoiding harsh chemicals or environments during storage. Following these tips will help improve durability and functionality of the metal sheets.
Cleaning and inspection techniques
As far as cleaning and inspecting galvanized metal sheeting is concerned, I advocate a straightforward and meticulous method that tends to its longevity and functionality. Here’s what I pinpoint based on my experience:
- Regular Cleaning: To clean, start with the warm soapy water and wash the surface. Do not scrub it using cleaning aids that have a rough surface because this may lead to scratches on the zinc coating. Soak a clean cloth or a soft sponge in warm water and use it for gentle scrubbing on the surface to get rid of any grime or material.
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals:Refrain from using strong cleaning aids that have acid or alkalis in them as well as ammonia or chlorine since those are likely to destroy the galvanized layer. For stubborn marks, using diluted white vinegar and water may work as a more gentle option.
- Thorough Rinsing and Drying: Ensure there is clean water available so that the metal sheets may be washed thoroughly after use. The sheets should then be patted with a soft towel or left to rest in an area with good aeration so moisture and water spots are avoided as much as possible.
- Visual Inspection: Split-rust stains should be identified and rectified instantly. These stains should be sanded down using a wire brush or a fine sander, and a protective zinc-rich coat of paint or primer should be used to cover the sanding area.
- Check for Corrosion or Rust: In my opinion, maintenance cleaning of the metallic sheeting should be done on a minimum of every six month rotation. However, the inspection frequency should be boosted if the metal is exposed to conditions of high moisture, salt, or industrial pollution.
- Routine Scheduling: It is prudent to refresh the inspections of the metal sheeting at least twice a year. In cases of high moisture, salt air, or industrial emission exposure, more frequent periods of inspection may be necessary.
When following the procedures outlined here, your galvanized metal sheeting will stay in tip-top shape for years to come. It all comes down to managing a light cleaning habit while simultaneously balancing on a very detailed inspection regimen to solve and mitigate issues as early as possible.
Addressing scratches and minor damage
In order to fix scratches and minor damages on galvanized metal sheeting, one needs to start by cleaning the scratched area with soapy water. Once it dries, lightly sand the area to remove any oxidized loose zinc or rust. Finally, use a touch-up paint or primer made for galvanized surfaces. There is a specific touch-up aid used for applying zinc paints, which ensures that the protective coat is maintained, while the strength and life of the metal “touched-up” aids.
Extending the lifespan of galvanized steel products
To prolong the life of galvanized steel products, I personally recommend a mixture of routine maintenance and preventative protective measures. I believe that regular inspections are critical in identifying scratches, rust spots, orbits of debris, and accumulation early on. Periodically washing the surface with a gentle detergent prevents contaminants from degrading the zinc coating. Furthermore, good ventilation and drainage in installations reduces the exposure to moisture, which is a common cause of corrosion. For environments where the conditions are more hostile, I recommend backup coatings or sealants for added protection. If proactive practices are maintained, the performance and life span of galvanized steel products can be greatly improved.
What factors should be considered when choosing galvanized steel sheets?

While opting for galvanized steel sheets, a few factors like the environment the material is going to be used in, and the zinc coatings on the steel sheet, which determine its corrosion resistance, need to be analyzed. Assess the sheet’s intended application, including structural or aesthetic applications, as well as other materials it will be used in to evaluate galvanic corrosion compatibility. Finally, check the quality standards and certifications to verify the level of consistency in quality and performance to xi.
Gauge and thickness options
In regards to gauge and thickness choices, I always point out that the sheet’s details ought to fit the project requirements within the confines of the specific scope. It is a known fact that stronger and thicker sheets have more strength and durability, thus, they are used for heavy construction and extreme environmental conditions. On the other hand, thin sheets are more appropriate for light weight structures or where ease of fabrication and modification is needed. In my experience, the most efficient balanced approach to meeting the structural needs and striving for resource efficiency aim is the selection of proper gauge or thickness of galvanized steel sheets.
Coating thickness and quality
The performance and service life of galvanized steel sheets are influenced heavily by the coating thickness and quality. A thicker coating yields superior corrosion resistance which is desirable for highly humid or severely exposed environment situations. Yet again, the application in question must guide the choice; an indoor, low risk environment does not warrant overly thick coatings. Maintaining consistency of coating quality through set standards like ASTM or ISO provides assurance and protection across all applications.
Specific environmental considerations
the approach to specific ecological issues begins with the environmental context on which the project is sited. For example, coastal regions have higher levels of salt and moisture, which necessitates the use of galvanized rusting steel sheets with a high corrosion resistance to prevent premature failure. On the other hand, I suggest using industrial coats for chemical or pollutant exposed environments for more robust protection. In addition, one must also account for the bounds of temperature interesting—the highest and lowest extremes of temperature affect component behavior and the protective coating. Adjusting the materials specification to correspond with these environmental conditions will most certainly lead to enhanced performance, durable components, and extended service life.
Are there any limitations or drawbacks to using galvanized metal sheeting?

Although galvanized metal sheeting is highly corrosion resistant and durable, there are some trade-offs. The zinc coating tends to erode in highly abrasive or acidic environments, exposing the steel underneath to corrosion. Furthermore, some finishes and welding techniques may not be possible due to the metal’s galvanization, which will require more strategy during fabrication. Lastly, untreated steel is less expensive initially but alongside the longer lifespan of galvanized steel, it offsets the initial investment. Considering these factors makes sure the specific requirements of the project are met.
Potential issues in extreme environments
I can attest to the fact that galvanized metal sheeting does work well within a myriad of environments but performance, especially in extreme conditions, can be a challenge. For example, coastal or marine environments have salt water and salty air. When exposed over prolonged periods, these can deteriorate the zinc coating and zinc’s protective qualities over time. Moreover, industrial settings with elevated levels of acidic or alkaline substances can be detrimental too. Expecting the coating to last without some form of additional maintenance or protective measures is naive. Each of these scenarios requires meticulous evaluation, and sometimes, the incorporation of alternative materials or additional protective measures to prolong performance.
Compatibility with other materials
Galvanized metal sheeting has relatively fewer restrictions when combined with various construction materials such as wood, concrete, and almost all forms of steel. However, issues copper and brass pose when these two materials are in contact with anything and everything moist, makes pairing more complicated than one thinks. To help avoid any corrosion, these metal components require adequate non-conductive barriers or protective coatings to prolong the structure’s life.
Addressing common misconceptions
It comes with no shocking surprise that, as an industry expert, there are a number of myths that come up in regards to galvanized metal sheeting that, more often than not, require precise clarifications. For instance, galvanized coatings are often correlated with corrosion proof metal; a logic that is completely irrational. While galvanization does provide some form of resistance, especially in comparison to the more extreme atmospheric conditions, it still lacks immunity. Via improper maintenance or prolonged exposure to extreme environmental conditions, corrosion can, and will, take place. Another myth that needs disproving is the notion that neither copper nor brass can be galvanised, and, as a consequence, used with other metals. This idea holds some accuracy, however, compatibility can be tackled with the help of barriers or coatings, which makes it impossible for the galvanic reaction – which results in corrosion – to take place. Equipped with the right information and a little preparedness, all of these myths can be effectively tackled in order to maximize the efficiency and lifespan of galvanized materials in construction as well as industrial uses.
Reference
- Rainville-Carlson: Galvanized Sheet Metal Roofing – This source provides insights into the durability and style of galvanized sheet metal roofing.
- BB Roofing Solutions: Best Corrosion-Resistant Metal Roof Materials – Discusses various corrosion-resistant roofing materials, including galvanized options.
- Mid Michigan Metal Sales: Do Metal Roofs Rust? A Complete Reference Guide – Explains the rust resistance of galvanized and Galvalume steel roofing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is galvanized steel sheet metal and how is it made?
A: Galvanized steel sheet metal is a type of steel that has been coated with a protective layer of zinc. It is typically made through a process called hot-dipping, where steel sheets or coils are immersed in a bath of molten zinc. This process creates a corrosion-resistant surface that offers excellent protection against rust and other forms of degradation.
Q: What are the benefits of using galvanized steel for roofing?
A: The benefits of galvanized steel for roofing are numerous. It offers superior rust and corrosion resistance, extending the lifespan of the roof. Galvanized steel is also durable, cost-effective, and easy to work with. It’s an ideal choice for outdoor applications due to its ability to withstand various weather conditions. Additionally, galvanized steel is recyclable, making it an environmentally friendly option.
Q: How does hot-dipped galvanized steel differ from other types of galvanized steel?
A: Hot-dipped galvanized steel is known for its superior corrosion resistance compared to other galvanizing methods. The process involves immersing the steel in molten zinc, creating a metallurgical bond between the steel and zinc. This results in a thicker, more durable coating that provides better protection against rust and corrosion than electroplated or pre-galvanized steel.
Q: What is the difference between white rust and red rust on galvanized steel?
A: White rust is a form of zinc corrosion that appears as a white, powdery substance on galvanized steel. It typically occurs when galvanized products are exposed to moisture during storage or transportation. While it can affect appearance, white rust doesn’t usually compromise the steel’s structural integrity. Red rust, on the other hand, indicates that the zinc coating has been compromised, and the underlying steel is corroding. This is more serious and can affect the material’s strength and durability.
Q: How long does galvanized steel roofing typically last?
A: The lifespan of galvanized steel roofing depends on various factors, including the thickness of the zinc coating, environmental conditions, and maintenance. However, high-quality galvanized steel roofing can last anywhere from 40 to 70 years with proper care. In less corrosive environments, it may even last longer.
Q: Can galvanized steel sheet metal be painted?
A: Yes, galvanized steel sheet metal can be painted. However, it’s important to properly prepare the surface before painting to ensure good adhesion. This typically involves cleaning the surface, allowing it to weather for several months, or treating it with a special primer designed for galvanized steel. Painting can further enhance the corrosion resistance and customize the appearance of galvanized steel structures.
Q: Is galvanized steel sheet metal suitable for all climates?
A: Galvanized steel sheet metal is highly versatile and can be used in most climates. However, its performance can vary depending on the environment. It performs exceptionally well in rural and suburban areas but may require additional protective measures in highly industrial or coastal areas where exposure to corrosive elements is higher. Consulting with a roofing professional can help determine the best solutions to meet your specific climate needs.
Q: How does the cost of galvanized steel roofing compare to other roofing materials?
A: Galvanized steel roofing is generally more cost-effective than many other roofing materials, especially when considering its longevity and low maintenance requirements. While the initial cost may be higher than some options like asphalt shingles, its durability and longer lifespan often result in lower long-term costs. Additionally, the energy efficiency of reflective galvanized steel roofing can lead to reduced cooling costs in warmer climates.