When purchasing pipes for a project, it is essential to understand the differences between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 pipes, as this is vital for adhering to best practices for optimal performance and safety. While these two very popular pipes may look similar at first glance, they differ significantly in terms of wall thickness, pressure capacity, and where they are used or can be used. Selecting the right pipe to use is dependent on a great number of factors, including meeting the project’s special requirements and matching materials. Within this paper, the major differences between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 pipes will be explained in detail to enable you to make informed decisions for the work that requires piping. So whether you are a plumbing expert, are working in industrial applications, or engaged in construction works, this knowledge will be beneficial as it will prevent a huge loss of time and expenses or possible conflicts in the future.
Overview of Schedule 40 and Schedule 80

The primary differences between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 pipes primarily lie in their wall thickness, pressure ratings, and material composition. Schedule 40 pipes have very thin walls; therefore, they are lightweight and are used in low-pressure applications, such as ventilation, irrigation, and residential water circulation systems. In contrast, Schedule 80 piping is provided with thick walls, which include high pressure ratings due to higher pressure applications, including industrial processes and chemical transport systems. The sizes of the outer diameters for both pipe schedules are standard, but this varies in the inner diameter due to the difference in thickness of the walls. If a project requires an increase in wall thickness to enhance resistance or performance in very demanding situations, then Schedule 80 is generally the answer. Nevertheless, if lightness in weight, term of durability and cost efficiency are key priorities, then Schedule 40 is normally preferable.
Definition of Schedule 40 and Schedule 80
Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 are sizes given for standardization purposes that define the pipe wall thickness and pressure handling ability. Pipe schedules are similar to standards and most of them are originally set by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) and are critically important due to ensuring fitness for purposes in optimal plumbing, non-residential and industrial, and plumbing.
Thinner walls with larger inner diameters define schedule 40 pipes, which makes them more effective to use in applications with lower pressure or where cost and material efficiency are priorities. For example, in domestic plumbing systems or sewers, schedule 40 is frequently employed because its strength is adequate and therefore imposes low material costs.
On the other hand, Schedule 80 pipes have thicker walls that are designed to withstand higher service pressures. And such are found in high pressure flow systems, chemical handling plants, and cataclysmic environments where high temperature, mechanical and physical stress, and chemical exposure are in abundance. The problem, however, is this additional weight and wall thickness reducing the pipe’s ability to have a large internal diameter.
Note that the outer diameter is the same for an equal nominal size of both schedule 40 and schedule 80 pipes; the distinction is the decisions about strength as opposed to flow allowance. For instance, an engineer or contractor can delightfully use these standards in the design with respect to material selection since it allows for a high level of flexibility with specific operational requirements.
Key Differences Between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80
|
Parameter |
Schedule 40 |
Schedule 80 |
|---|---|---|
|
Wall Thickness |
Thinner for the same nominal size |
Thicker for the same nominal size |
|
Internal Diameter |
Larger due to thinner walls |
Smaller due to thicker walls |
|
Pressure Rating |
Lower pressure tolerance |
Higher pressure tolerance |
|
Weight |
Lighter |
Heavier |
|
Flow Capacity |
Higher due to bigger diameter |
Lower due to smaller diameter |
|
Cost |
Generally less expensive |
Typically more expensive |
|
Strength |
Moderate for general applications |
Higher for demanding applications |
|
Applications |
Low to moderate pressure systems |
High-pressure or industrial systems |
|
Temperature Resistance |
Suitable for standard temperature ranges |
Better for higher temperature ranges |
|
Durability |
Adequate for general use |
Superior for harsh environments |
Why Choose Schedule 40 or Schedule 80?
The decision concerning whether to use schedule 40 or schedule 80 piping usually hinges on the particular application considerations. Schedule 40 pipes are typically applied in residential or light commercial activities because of the moderate strength of the pipe as well as the cost and the appropriate pressure and temperature for normal pressure piping. Typically, they are installed in such areas as water lines, irrigation lines, and a few chemical transportation lines where the importance of pressure is marginal.
Physical Characteristics of Schedule 40 and Schedule 80
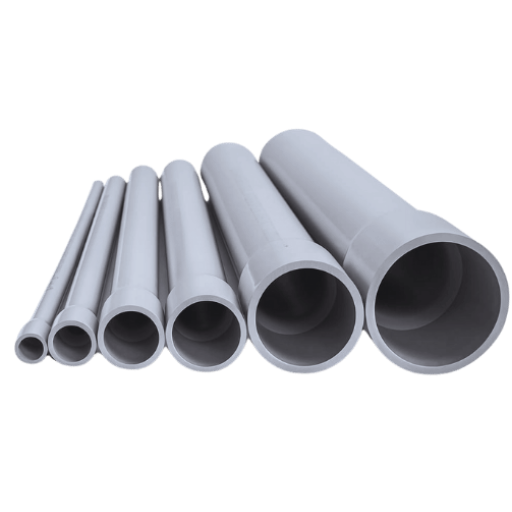

The most prominent difference in the physical construction of Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 pipes occurs because of the wall thickness. In comparison, Schedule 80 pipes have great wall thickness, meaning they can resist higher pressures than Schedule 40. For this reason, there is a consequential reduction of the internal diametric capacity of the schedule 80 pipes in relation to the schedule 40 pipes of the same nominal size. Furthermore, the thicker tube walls of the schedule 80 pipes do not come without limitations over and above the limitations of the thinner wall schedule 40 pipes because they tend to have additional material weight, hence reducing the flow capacity of the fluid. Both pipes can typically be found in PVC and steel materials, and the choice between these two is solely based on the pipes that would be capable of withstanding the pressure of the application or the environmental conditions in which the pipes are used.
Thickness Comparison: Schedule 40 vs Schedule 80
The primary difference between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 pipes is the difference in the wall thickness, which dictates how the piping will perform and how it will be used. For instance, it may be noted that Schedule 40 pipes, in 1 inch of PVC, have a thickness of around 0.133 inches, while the same size of Schedule 80 would have a thickness of around 0.179 inches. And it is this thickness that makes it possible for the Schedule 80 pipe to be rated for much higher pressures than normal. Usually, 1-inch pipe schedule 40 PVC is rated for about 450 psi pressure, whereas, for the same size schedule 80, it can handle 630 psi. This is where Schedule 80 is advantageous over 40, as the latter can be used for general residential applications with standard pressure ratings, where the former can be employed for sectional applications with higher pressure ratings. Understanding these measurements is imperative for the effective selection of the appropriate pipe schedule for the specific operational requirements.
Material Durability and Resistance
The endurance and hardiness of a material are subject to the material’s composite structure, both its integrity and behavior, as well as its response to environmental influences, including, particularly, the pressure and temperature, and chemical compounds as well. For example, PVC pipes tend to be corrosion and abrasion resistant, and as such, it’s considered an ideal material for the supply of large amounts of water, chemicals, or other fluids in homes and industries. On the other hand, they also have superb mechanical and thermal attributes, in particular steel and stainless steel, which are capable of withstanding very high pressure and temperature deformations without deformation problems. Improvements and innovations in the field of materials, however, have also brought about the use of materials such as composites and reinforced polymers. Such materials, which are light, are very strong and good for use in the construction and aviation industries, among many others.
Pressure Ratings for Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 Pipes
This pipe wall thickness is calculated most accurately in the cases of Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 according to some specific rules, which include client, material, and pipe sizes. PVC and CPVC pipes typically exhibit different working pressures by construction. Therefore, as the temperature goes up, the working pressure in both Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 pipes decreases. It is standard extrapolation to claim that at 40°C, the pressure capacity of an operating PVC pipe will decrease by as much as 50% when compared to that pipe under normal room temperature, and temperature de-rating factors must be included as well.
Another important factor with respect to pressure ratings is the size of the pipes. Smaller pipes are more pressure-resistant than larger pipes when the pipe wall thickness is related to the diameter. In simpler terms, a ½-inch Schedule 80 pipe will withstand higher pressure, so you should consider the implications before consulting a Schedule 80 pipe. This implies a requirement of technical calculation to establish proper pipe match given the use in different applications.
Applications of Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 Pipes

Applications of Schedule 40 Pipes:
- Water Distribution Systems
It is very common to see Schedule 40 pipes being used mainly for residential and commercial water systems because low-pressure applications do not require very thick walls, reducing costs and simplifying their installation. They can be applied in virtually all systems operating at moderate pressures.
- Drainage and Waste Systems
These will suit applications with low pressures, such as wastewater drainage, and such systems are found in both domestic buildings and in different environments.
- Irrigation Systems
In pressurized piping systems where the pump only produces small pressure drops and long distances and low-powered pumps are used, and where the silica needs to be transported in bulk for substantial distances in the appropriate pipe, Schedule 40 PVC is employed.
- Ventilation and Low-Pressure Air Systems
Due to their lightweight and lower pressure rating, Schedule 40 pipes are mostly used in specific air movement systems in industries or for HVAC applications.
- Aquarium and Fish Farming Systems
The partition of Schedule 40 pipes is such that there are expansions and flexibilities that are advantageous in their use in water circulation systems for fish farming settings.
Applications of Schedule 80 Pipes:
- High-Pressure Liquid Transport
Companies using high-pressure fluid transfer systems rely considerably on the increased thickness of Schedule 80 pipes for reasons of longevity and additional resistance to pressure.
- Chemical Processing Systems
Schedule 80 pipes, especially those of CPVC or other chemical-resistant materials, are intended for the transport of aggressive chemicals, acids, and bases.
- Industrial Compressed Air or Gas Systems
In potentially hazardous conditions such as some industrial compressed air systems, these pipes can handle thin support pipes at high pressures without bursting.
- Underground Installations
Reinforced Schedule 80 pipes are more reliable for such purposes, where blind forces such as the weight of surrounding soil or vehicular loads greatly stretch the pipeline in the horizontal direction, especially when laid underground.
- Hydraulic Systems
Common Uses in Construction and Plumbing
Schedule 80 is very popular in construction and plumbing applications mainly because of its effectiveness in carrying fluids under extreme pressure and being thick enough to cope with a harsh environment. An interesting area in the construction sector is its use in construction support areas as the work is undertaken, providing stress and tensility of the material. They can accommodate both relatively low internal and external forces, which makes them the best material to use in the construction of piers, temporary elevated working platforms and for making frameworks that will support loads. As less reliable material, the Sandwich beams have this alternative quality (load-supporting shapes) at the edge, which is reinforced by the fibers but still entails a made-to-order design.
As far as plumbing is concerned, water and wastewater flow in both directions, but as soon as top down, which is normal, and chemical plumbing falls within the very top of the schedule; therefore, with regard to the topic here, the principles or construction of these pipes are common for all levels. Those higher pressure systems include systems for residential or industrial purposes, clean, low flow pressure water, non-volatile chemicals such as alcohol, organic solvents, or energized liquids like effluent, and many more. Schedule 80 within a structure consists mostly of elements that consist of static structures. One of those structural elements that consists the support system made of II-C beams not containing the static retreat regions is a beam of varying breadth, plan profile, and materials, such as PVC pipes and boards with plywood on their floor or walls
Industrial Applications of Schedule 80 PVC
- Chemical Processing:
In chemical processing plants, Schedule 80 PVC is the most preferred for its superior ability to resist most of the acids, bases, and solvents in normal pH and temperature ranges. It might be possible to use Schedule 40 with special fittings and/or adhesives, but that is more likely to be a temporary fix. Based on some information, Schedule 80 is capable of handling chemical media within a pH range from 1 to 14 at the specified temperatures.
- Water Treatment Facilities:
This material is very efficient in this context, also as in the case of chlorine, and other water treatment chemicals in water purification, and/or effluent treatment pipe installations. Furthermore, the piping systems in these conditions will work under high pressure,s which require reinforcement and additional support for the pipe joints. For example, the industrial arrangements involve flow rates and pressure ratings meeting the defined requirements, i.e. pipes with a dimensional size of 2 inches frequently go up to 280 psi at the pressure end of the assembly.
- HVAC Systems:
Furthermore, USA clients have a practice of utilizing schedule 80 pvc systems for their needs in HVAC systems where chilled and hot water are used, and further within condensate drainage lines. The material can easily withstand up to 140°F (60°C), which allows it to cope easily while reducing the chances of failure in temperature operating environments.
- Agriculture and Irrigation:
In application in an agricultural industry, the lightweight yet sturdy essence of the encasement elements is considered as useful for the installation of irrigation or drainage channels. It remains available, offers easy access to water, and stands up well to the use of chemicals such as fertilizers and pesticides, which are known to be corrosive and do not decompose. It was found that interconnected piping systems made of Schedule 80 PVC have maintained their integrity for the entire outdoor extension.
- Industrial Manufacturing:
Textile, paper, and food processing industries are inevitably in need of Schedule 80 PVC for the transportation of water and process media and fluids. This is credited to its mortar’s clean, smooth surface, which does not harbor developing scale, enhancing the span of a liquid, ensuring an effective conveyance in a pipeline.
- Power Plants:
For instance, in power plants of the thermal and hydro (water) kind, Schedule 80 PVC is extensively used in the cooling water and services on a high-pressure steam station. Since it has little or no dielectric loss, improved safety could be associated with its use near electric/electrostatic equipment.
Cost Considerations for Schedule 40 and Schedule 80

The differences in cost spreading between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 can be attributed to their wall thickness and corresponding material standards. It thus goes without saying that Schedule 80 pipes are in a higher price range than their counterparts, Schedule 40, since the former has wider bases and can bear higher pressure loads. Additional costs can be accrued in cases where high-pressure resistance and strength are required, as is the case in complex structures and industrial conditions.
On the contrary, Schedule 40 pipes are cost-effective and recommended for areas where little pressure is used, hence they are most of the time applied in residential drain pipes and other easy fluid carrying systems. While the choice between the two takes into account the price at the beginning, it is also considered if they can match the project-specific requirements, going further in that an underspecified pipe means more cost in terms of repairs and maintenance, or even the system collapse can be experienced in due time.
Price Comparison: Schedule 40 vs Schedule 80
Upon the analysis of the price differences between Schedule 40 and 80 pipes, it can be said that the element that affects the cost the most is material thickness and capacity. Because of their more sophisticated, high-quality, and higher liner material, Schedule 80 pipes are usually more expensive than Schedule 40 ones. For example, according to the recent market, the price of 1.5-inch Schedule 40 PVC pipe can approximate $1.50 per linear foot, but the same wall in Schedule 80 pipe costs about $2.20 per linear foot.
Here, additional costs are essentially the cost of materials used to enrich the thicker walls at the Schedule 80 level pipe. Also, this is because the pressure ratings that these pipes offer are enhanced. Although the procurement cost of Schedule 80 pipes is high, in the majority of such situations, their durability and strength prove beneficial. An example is in the case of various systems, including industrial systems and chemical plant systems. Hence, while low-pressure residential buildings have no choice but to use Schedule 40 due to cost considerations, industrial structures prefer to use other types of pipelines since the situation considers both the strength and the cost. However, it is always necessary to comprehensively check the tradeoffs between initial monetary investment and system expectations to deal with such challenges.
Long-term Cost Efficiency
Any economic analysis of the life of a pipelining system will also take into account the lifetime of the material, maintenance, and reliability of the system in question. Schedule 80 fittings, which have high pressure capacities and thick walls, have resisted erosive situations better, and there are intervals in their utilization in severe environments, which may mean less costs from replacement and maintenance. While the durable schedule 80 pipes are costly and have limitations of use, schedule 40 pipes have lower costs and design limitations to pressure retention and, as such, are replaced more regularly and provide more satisfactory service because of the lower initial costs.
Choosing the Right Pipe for Your Project

When selecting the right pipe for your project, consider the following key factors:
- Application Requirements – In order to understand what the pipe shall be utilized for, it is important to consider the working pressures or the nature of the processes being handled. For instance, where pipes shall connect high-pressure water to flow, they mostly recommend being Schedule 80, where low-pressure plumbing or even irrigation could still work with Schedule 40 pipes.
- Material Compatibility – Knowledge about the substances that the pipe will be made to carry, such as water, gas, and chemicals, is also important. For example, PVC is often chosen as a material for pipes dealing with water on account of being a chemical delivery system, while high temperatures may require metal substance for the purpose of lining them to reduce corrosion.
- Pressure and Temperature Ratings – Appropriate examination of the pipe ratings in relation to the operating conditions of the system in terms of pressure and temperature should be done to enable safety and serviceability.
- Cost and Budget – Comparing the cost and budget of using materials against short-term and long-term loss, explained by other consequences of improper selection of pipes, including opportunities given by the usage of better pipes, which would prevent leaks and failures at a reduced cost.
These factors do not let them be of vital importance and create a method in which to select a component based on its functionality and cost while within the confines of the budget.
Assessing Project Requirements
Assessing the requirements of a project accurately is an important step in the successful completion of any pipework. Prioritize completing a detailed analysis that is concerned with the objective of the system, the expected operating conditions, and external factors that might affect the system. In the simplest of terms, pipes designed for high-pressure activities should be stronger to withstand the force they will be subjected to, whereas facilities handling chemicals or any other form of corrosive matter may necessitate the utilization of materials such as stainless steel or specific polymer materials in order to prevent corrosion. Furthermore, one has to look at standards and requirements enforced either per the law or by the industries in an analysis so that health and performance safety is not jeopardized. Development of superior materials, such as reinforced thermoplastics or the use of corrosion-resistant alloys in designs, makes it possible to address both durability and cost. With the help of a checklist that breaks these necessities down into a project agenda, the users can effectively make use of the tools they have at their disposal for purposes of enhancing dependability, efficiency, and effectiveness with regard to the selected systems.
Guidelines for Selecting Between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80
When the decision is being made as to whether to use Schedule 40 pipes or to go with Schedule 80, there is a need to have knowledge of the properties of the material employed, the pressures at which the pipes can be used, as well as the use-specific requirements. For low-pressure types such as plumbing, irrigation and ventilation, Schedule 40 pipes are characterized by smaller walls. They also incur lower charges in terms of transportation and manufacturing due to less material usage and the weight of the item, which is very useful when faced with low-pressure demands such as in the residential setting.
On the contrary, Schedule 80 code has thicker walls, which provide a higher strength and capacity to withstand more pressure. These kinds of pipes are good in industrial settings, in dealing with chemicals or high-pressure fluids and gases. Nevertheless, this type of pipe is rather expensive to procure and install than schedule 40 pipes because the internal flow holes are much greater for schedule 40 than schedule 80 pipes planing the material per volume, with the volume being the flow area, shall result in greater cost returned for the schedule 40 pipes by far compared to schedule 80 pipes.
Reference Sources
-
Water Requirements in Growth Stages and Effects of Deficit Irrigation:
- Key Findings: This study explores irrigation schedules with varying efficiency rates (40%, 60%, and 80%) for agricultural applications. It highlights the impact of these schedules on fruit productivity.
- Read more
-
Failure Analysis on Slinger Disk Pipe of Purified Terephthalic Acid Vessel:
- Key Findings: This paper analyzes the failure of pipes under different loads, including pipes with Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 specifications.
- Read more
-
Strength Properties of Polymer Reactive Powder Concrete with Waste Materials:
- Key Findings: The research investigates the use of waste materials in concrete, focusing on replacement percentages like 40% and 80%.
- Read more
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the difference between schedule 40 and schedule 80 pipes?
A: The main difference between schedule 40 and schedule 80 pipes lies in their wall thickness. Schedule 80 pipes have a thicker sidewall compared to schedule 40 pipes, which allows them to withstand higher pressure ratings. This makes schedule 80 pipes more suitable for pressurized liquid applications, especially in industrial settings. In terms of nominal pipe size, both schedules share the same outside diameter, but the inner diameter of schedule 80 is smaller due to its increased wall thickness. When choosing between these two options, consider the specific pressure requirements and whether the application might be subject to physical damage.
Q: How does the thickness of schedule 80 PVC compare to schedule 40 PVC?
A: Schedule 80 PVC has a greater wall thickness compared to schedule 40 PVC, which enhances its durability and pressure tolerance. This thicker wall means that schedule 80 can handle higher pressures, making it ideal for applications where fluid pressure is a concern. In contrast, schedule 40 is sufficient for lower pressure systems, such as water pipes in residential plumbing. The difference in thickness also results in schedule 80 being heavier and more robust. When selecting between these two types of PVC, consider the nature of your project, particularly whether it involves high-stress conditions or potential physical damage.
Q: Can I use schedule 40 fittings with schedule 80 pipes?
A: Yes, you can use schedule 40 fittings with schedule 80 pipes, but there are some considerations to keep in mind. Since schedule 80 pipes have a thicker wall, you may need to ensure that the fittings can accommodate the different wall thicknesses. While the outer diameter remains the same, the inner diameter of a schedule 80 pipe is narrower, which can affect fluid flow. It is essential to ensure that the fittings and joining methods used are compatible with the pipe’s pressure requirements. For critical applications, using fittings that match the pipe schedule is often recommended to avoid issues related to pressure stress and overall performance.
Q: What are the pressure ratings for schedule 40 and schedule 80 pipes?
A: Schedule 40 and schedule 80 pipes have different pressure ratings based on their wall thickness. Schedule 80 pipes can handle significantly higher pounds per square inch (psi) ratings compared to schedule 40 pipes, making them suitable for applications involving high-pressure fluids. For instance, schedule 80 PVC is often used in industrial plumbing systems, where pressure and stress are critical factors. Schedule 40, while adequate for many residential uses, may not provide the same level of safety and reliability in high-pressure scenarios. When selecting pipes, always consult the ASTM standards for the specific pressure ratings associated with each schedule type.
Q: Are schedule 80 PVC pipes overkill for residential plumbing?
A: Using schedule 80 PVC pipes for residential plumbing can be considered overkill in most cases, as schedule 40 typically suffices for standard water supply and drainage systems. However, if a home is located in an area prone to physical damage or if the plumbing system will carry fluids under high pressure, schedule 80 may be justified. The thicker walls of schedule 80 provide enhanced protection against impact and wear, which can be beneficial in certain environments. Ultimately, the decision should be based on the specific plumbing requirements, pressure ranges, and potential for physical damage.