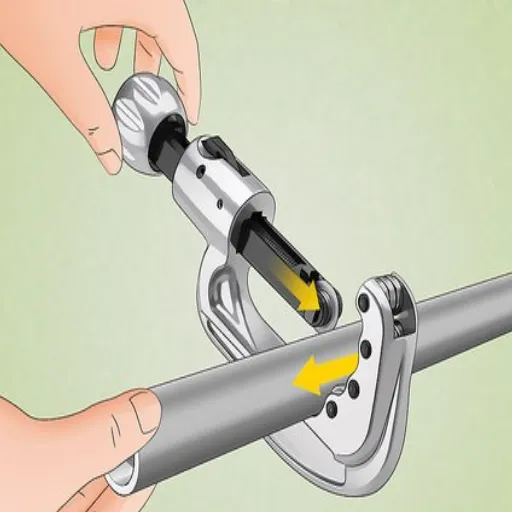
Stainless steel is a durable, highly functional material that finds application in construction, automotive, and home improvement projects. Nevertheless, its durability and corrosion resistance present a challenge to cutting. Professionals and home users who undertake do-it-yourself projects stand to gain a lot in terms of time, effort, and money by knowing and applying the best methods for cutting stainless steel. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll provide step-by-step approaches to techniques, must-have tools, and cutting hacks that enable you to cut stainless steel in both a safe and precise manner.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Project
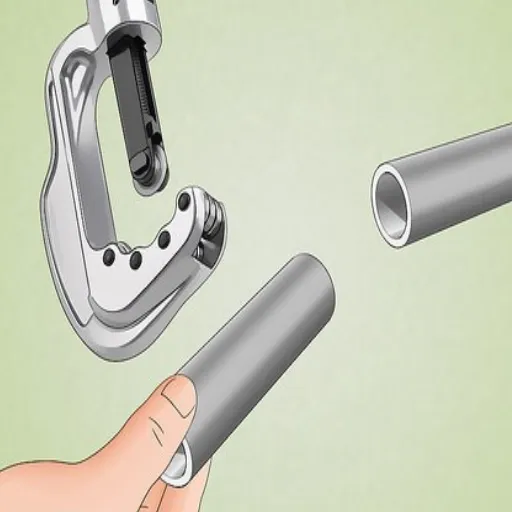
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Tool
Material Thickness and Type
Identifying the appropriate size and type of material for the project is the first step in steel cutting:
- Thin sheets: Tin snips or electric shears for deformation-free, sharp cuts
- Thick pipes and sheets: Angle grinder with metal cutting disc or plasma cutter
Precision Requirements
- Delicate or detailed cuts: Laser cutter or water jet cutter for extraordinary precision
- Standard productivity cuts: Power tools such as a jigsaw with a metal blade
Safety and Operation Complexity
- High-power tools: Generate heat, sparks, or flying debris – require proper safety equipment
- Manual tools: Much safer for novices, but less flexible in applications
Pros and Cons of Each Cutting Method
Power Tools – Pros
- Efficiency and Speed: Quick and accurate cuts
- Multifunctionality: Interchangeable blades for various materials
- Precision: Laser guides and digital measuring systems
Power Tools – Cons
- Safety Hazards: Require proper training and safety gear
- Accessibility and Cost: High initial investment
- Complex Maintenance: Regular cleaning and blade replacement
Manual Tools – Pros
- Safety: Lower injury risk for inexperienced users
- Cost-Effective: Low purchase price, minimal maintenance
- Portability: Lightweight and easy to transport
Manual Tools – Cons
- Limited Effectiveness: Difficult with heavy or thick materials
- Physical Stress: Causes fatigue during extended use
- Slower Pace: Time-consuming for large projects
Advanced Technologies – Pros
- Automation: Can operate without supervision
- Precision: High accuracy with minimal material waste
Advanced Technologies – Cons
- Training Requirements: Need specialized certification
- Equipment Cost: High investment with slow ROI
- Maintenance Complexity: Expensive upkeep
Best Options for Thin vs. Thick Stainless Steel
| Aspect | Thin Steel | Thick Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Tools | Tin Snips, Jigsaw, Laser | Plasma, Waterjet, Band Saw |
| Accuracy | High | Moderate to High |
| Efficiency | Moderate | Fast |
| Expense | Low to Moderate | High |
| Heat Effect | Low | Moderate |
| Finishing | Minimal | May Be Needed |
| Usage | Intricate, Curves | Heavy-Duty, Straight |
Step-by-Step Instructions for Cutting Stainless Steel

Preparation Steps Before Cutting
- 1Select the Right Cutting Tool: Choose appropriate tools based on material thickness – precision tools for thin sheets, powerful tools for thicker materials.
- 2Ensure a Stable Work Surface: Use a cutting bench or designated work surface to prevent material sliding and ensure quality finish.
- 3Measure and Mark Accurately: Use a permanent marker or a carbide-tipped scribe with good contrast. Always double-check measurements.
- 4Clamp the Steel Appropriately: Secure the stainless steel sheet to prevent vibrations and promote accuracy.
- 5Use Safety Gear: Wear proper PPE, including safety goggles, gloves, and ear protection.
- 6Check the Tools: Ensure all tools function properly, and cutting blades are sharp and undamaged.
- 7Set Up the Cutting Area: Ensure adequate ventilation and remove flammable materials from the work area.
- 8Reduce Risk of Heat Damage: Manage heat-affected zones (HAZ) by covering adjacent areas or applying protective gels.
Executing the Cut
Throughout the operation, cutting stainless steel demands utmost focus on precision and safety. Follow these guidelines:
- Verify Equipment Setup: Ensure cutting equipment is correctly configured for the thickness and grade of stainless steel
- Maintain Proper Clamping: Keep the piece firmly secured to prevent vibrations or movements
- Use Consistent Pressure: Apply light, steady pressure to prevent overheating and blade wear
- Monitor Heat-Affected Zones: Control temperature to maintain material strength
- Continuous Inspection: Regularly check cuts against design specifications
Post-Cutting Tips for Clean Edges
Edge Finishing Techniques
- Remove Rough Surfaces: Use grinding wheels and spinning tools
- Precision Finishing: Apply chamfering tools for consistent edge finishing
- Quality Verification: Use calipers or edge profile gauges to check conformance
- Clean Edges: Remove oils, dust, and burrs with acetone or recommended solvents
Safety Precautions When Cutting Stainless Steel
⚠️ Essential Protective Gear
Personal protective equipment is crucial when cutting stainless steel to protect against sparks, sharp edges, and metal dust.
Required Safety Equipment
- Safety Goggles or Face Shields: Must comply with ANSI Z87.1 standards for high-velocity impact resistance
- Respiratory Protection: HEPA filter respirators or N95 masks in poorly ventilated areas
- Cut-Resistant Gloves: Kevlar or nitrile-coated gloves for protection against sharp edges
- Hearing Protection: Earplugs or earmuffs with 25+ dB Noise Reduction Rating
- Flame-Resistant Clothing: Sturdy, flame-resistant materials (avoid synthetic materials)
Working in a Safe Environment
- Proper Ventilation: Essential for removing harmful fumes
- Electrical Safety: Ensure all equipment is properly grounded
- Clear Walkways: Remove unnecessary items to prevent accidents
- Safety Signage: Mark hazard zones clearly
- Ergonomic Design: Use adjustable workstations to prevent musculoskeletal injuries
Common Hazards and Prevention
| Hazard | Prevention Measures |
|---|---|
| Slips, Trips, Falls | Clean spills immediately, use anti-slip mats, and inspect floors regularly |
| Ergonomic Injuries | Adjustable workstations, proper lifting training, and regular breaks |
| Chemical Exposure | Proper labeling, adequate ventilation, PPE, and MSDS training |
| Electrical Hazards | Qualified electricians, lockout/tagout procedures, and regular inspections |
| Fire and Explosion | Proper storage, fire suppression systems, and clear escape routes |
Avoiding Common Mistakes

Using the Right Tools
Selecting appropriate tools ensures safety, efficiency, and precision. Consider these factors:
- Assess task requirements before selecting tools
- Ensure proper tool maintenance and regular inspections
- Provide training on proper tool usage
- Follow manufacturer specifications and safety standards
Importance of Proper Preparation
Thorough preparation is crucial for project success and includes:
- Planning and organizing resources
- Risk assessment and mitigation strategies
- Utilizing modern data management tools
- Ensuring compliance with professional and safety standards
Tool Maintenance and Longevity
Best Practices for Tool Care
Maintenance Essentials
- Regular Inspection and Cleaning: Prevent debris, rust, and erosion buildup
- Proper Storage: Clean, dry environments to prevent moisture damage
- Lubrication: Apply appropriate oils or greases to moving parts
- Electrical Safety: Check cords and connections regularly
- Calibration: Follow manufacturer guidelines for specialized machinery
Extending Cutting Tool Lifespan
- Material Selection: Choose appropriate cutting materials (HSS, carbide, diamond)
- Operational Parameters: Maintain proper feed rate, spindle speed, and depth of cut
- Advanced Lubrication: Use high-pressure or minimum quantity lubrication (MQL)
- Precision Monitoring: Regular inspections with measuring devices
- Predictive Maintenance: Utilize IoT sensors and machine learning
When to Replace Tools and Blades
Warning Signs:
- Decreased performance and overheating
- Increased vibration affects accuracy
- Physical damage like chipping or deformation
- Excessive wear based on monitoring data
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the best way to cut stainless steel?
A: The best method depends on thickness and grade. Angle grinders work well for general purposes, laser cutting for precision, and hacksaws for thin sheets.
Q: Can stainless steel sheet metal be cut with a hacksaw?
A: Yes, especially for thin sheets and straight cuts. Use a high-quality metal blade designed for cutting metal.
Q: What tools are best to cut stainless steel?
A: Angle grinders, shears, and laser cutters are optimal. For thick sheets, use grinders with diamond or metal cutting blades.
Q: How can I avoid damage when cutting stainless steel?
A: Use proper blades, secure material with clamps, maintain steady pressure, and avoid excessive force to prevent warping.
Q: What is the most effective method for cutting thick stainless steel?
A: Angle grinders with metal cutting blades or plasma cutters are most effective for thick stainless steel.
Q: How do I make more accurate cuts in stainless steel?
A: Mark cutting lines accurately, start cuts properly, maintain steady hands, and use appropriate cutting guides.
Q: Do I need a deburring tool after cutting stainless steel?
A: Yes, deburring tools are important for finishing cuts and smoothing sharp edges or burrs.
Q: Can I use an angle grinder to cut stainless steel sink materials?
A: Yes, angle grinders are suitable. Use appropriate discs designed for stainless steel to minimize damage.
Q: What are common mistakes to avoid when cutting stainless steel?
A: Avoid using the wrong blade types, improper securing, excessive force, and inappropriate cutting angles.
Q: What are the best cutting techniques for stainless steel sheet metal?
A: Use shears for thin sheets, jigsaws for complex cuts, and plasma cutting for thick materials.
References
- Columbia University: Top Metal Cutting Blades for Demolition Masters
- Harvard University (ADS): Improvement of cutting performance for thick stainless steel
- MIT: Laser cutting metal parts
- University of Florida: Speeds and Feeds
- Stanford University: Machining Tools