Sandblasting stainless steel is a technology that marries accuracy, technical competence, and the right machinery to produce that perfect finish. If sandblasting is your method for cleaning corrosion, providing a smooth texture, or achieving a beautiful finish on stainless steel components, then this process is necessary for several industrial as well as decorative applications. This guide will provide comprehensive information about the sandblasting process for stainless steel, including its advantages, applications, and the equipment and techniques that yield the best results. After reading this article, you will understand how sandblasting both protects and decorates stainless steel, as well as the procedures that ensure safety and efficiency.
The Sandblasting Process
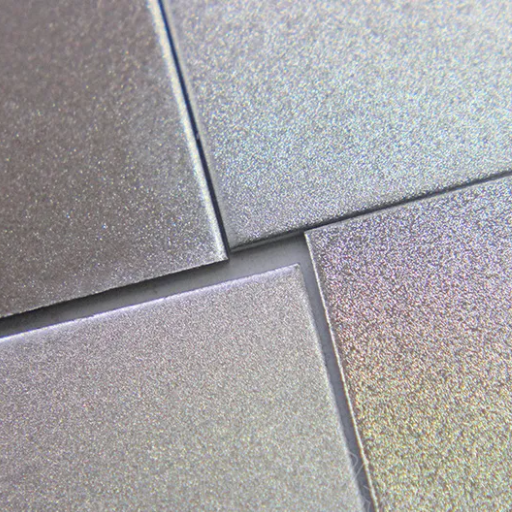
Sandblasting stainless steel consists of launching high-velocity fine abrasive against the steel surface by compressed air. These processes are done to clean, prepare, or texture the steel for different purposes. The stages include:
- Preparation: The stainless steel must be free from oil, grease, dirt, and contaminants before operations; otherwise imperfections may be formed during sandblasting.
- Abrasive Material Selection: Depending on the type of finish or degree of surface etching required, select the appropriate abrasives, such as glass beads or aluminum oxide.
- Equipment Setup: Perform all necessary equipment setup and preparation for proper operation. Ensure the use of established safety practices, wearing protective gear and operating ventilation systems, or maintaining clean air.
- Blasting Process: In order to get a uniform result and prevent the stainless steel from damage, the blasting shall hold an angle and distance all through; around 6 to 12 inches is preferred.
- Inspection: Check if the blasted surface texture is as desired and with the required cleanliness.
This ensures the best working procedure for enhancing the life and finish of stainless steel on accuracy and efficiency.
Introduction to Sandblasting
Abrasive surface preparation consists of cleaning, texturing, or preparing a surface with precision. The method is generally used for the high-pressure propulsion of abrasive materials, such as silica sand, aluminum oxide, or glass beads, to clean away contaminants like rust, paint, or scale on a wide variety of surfaces, including metal, wood, or concrete. Walnuts and garnet sand, zinc dust for sandblasting, and banana peels are some of the more unusual abrasives used to give the process a slight surface modification, increasing its roughness mainly, or helping to improve the adherence of a coating layer or welding.
Advancements in sandblasting technology have led to the design of more efficient equipment and environmentally friendly abrasives, resulting in fewer health hazards and less damage to the environment. For example, dust-suppressant systems have been integrated into the process to suppress airborne particles, thereby ensuring compliance with safety regulations while maintaining a cleaner work environment. Furthermore, these alternative abrasives, such as garnet and walnut shell, offer an environmentally friendly alternative to the hazardous crystalline silica sand, thereby further promoting the industry’s green agenda. Combining precise control and versatility, this technology finds applications from aerospace to construction.
Step-by-Step Sandblasting Procedure
- Preparation of the Work Area
Begin by securing the working area to ensure safety and efficiency. Clear out any unrelated objects from the vicinity, and protect all sensitive areas by covering them with protective sheeting to prevent any accidental damage. Establish a proper ventilation system or dust collection system of industrial grade to direct and control the release of particulate matter, thereby keeping the air clean.
- Inspection and Cleaning of the Surface
Look for existing cracks, rust, or contaminants on the surface that could endanger shear. Clean the surface of loose debris, oils, or any other residues using the correct cleaning agents or degreasers to ensure good adhesion for subsequent coatings.
- Setting Up the Sandblasting Equipment
Assemble the sandblasting machine, the blast pot, the compressor, and the abrasive media delivery system. The abrasive should be selected according to the surface type and finish requirements, such as aluminum oxide, garnet, or glass beads. Try to adjust the pressure of the equipment according to the hardness and density of the surface.
- Operator Safety Check
The operator of the apparatus must carry out the entire PPE protocol strictly. The operators have to wear a blast helmet with integrated respiratory protection, heavy-duty gloves, and a protective suit designed for sandblasting. All safety systems built into the equipment must be checked for proper function.
- Testing and Calibration
Try blasting on the test surface or at an inconspicuous spot on the face of the material. This allows adjustments of pressure, nozzle, and flow rate of abrasives in attaining desired surface profile without damage to the surface.
- Beginning the Sandblasting Process
The nozzle is positioned at an angle ranging between 45 degrees and 60 degrees; maintain an adequate distance from the surface, usually about 6-12 inches, depending on the equipment. Abrasive blasting should start with fluid, continuous strokes to cover the surface evenly. Never allow the abrasive jet to stay on a particular spot for too long, lest it cause over-blasting or deep gouges.
- Periodic Monitoring and Adjustment
Monitor the surface continuously to check for uniformity and prevent excessive removal of material. Refill abrasive media when required and inspect for blockage or wear inside the media delivery system that might affect performance.
- Post-Blast Cleaning and Inspection
After finishing the sandblasting process, clean it thoroughly to get rid of all abrasive residue using pressurized air or adhesive vacuum extraction. The surface is then inspected for evenness and to conform to the desired specification, for example, roughness (Ra) or clarity standard.
- Final Protective Measures
Benefits of Sandblasting Stainless Steel

- Improved Surface Preparation
The surface prepared by sandblasting is free from contaminants and dirt, rusted areas, and is clean and textured, ready for adhesion of further coatings or finishes.
- Enhanced Durability
As a distressing surface imperfection, sandblasting helps strengthen the stainless steel and reduces the chances of cracking or corrosion over a period.
- Aesthetic Appeal
In the desired interior or exterior, this process brings about a homogeneous, matte finish that can create further aesthetic value for stainless steel.
- Customization Options
Sandblasting allows the surface to be profiled to the extent needed by the project’s functional or aesthetic requirements.
- Time and Cost Efficiency
Improved Surface Texture
Sandblasting is used to improve texture by stripping materials of dirt, oxidation, or old coatings. It presents a level of surface that has been constructed through the sandblasting process, which roughens the surface. Such levels and roughness are vital in coating applications where adhesion to primers, paints, or sealants is ensured. Research studies have established that the roughened surface resulting from the sandblasting procedure increased the surface area for improved bonding strength of the new layer. The process also permits the fine-tuning of the extent of alteration to the surface, thereby allowing uniformity in performance and appearance under either industrial or architectural applications. The advanced abrasive materials and blasting equipment offer assurance that the surface preparation will meet stringent technical requirements.
Enhanced Durability and Corrosion Resistance
At its best, surface preparation is a rocket launch pad for durability and service life enhancement of the material to be coated. By dislodging dirt and grime, corrosion penetration, and old coating, it builds a clean, textured surface to which coatings or treatments will firmly grip. Studies and a crop of case studies reveal that properly treated surfaces prolong the lifespan of metallic constructions by suppressing corrosion onset and abrasion. Putting these further into consideration, it is really worth trying to combine corrosion-resisting coatings with modern surface treatment processes to reduce 50% maintenance, especially along with those who are exposed to severe environments, like for marine or industrial environments. These advances are very significant in preserving the execution of infrastructure elements and equipment when they are being subjected to extreme conditions.
Aesthetic Appeal of Sandblasted Finishes
Void of parental neglect accompanying a severe amount of duckling, sandblast finish has recently taken high honors for its clean, constant, and highly visual appeal. Sandblasting is surface treatment by controlled abrasion of various materials using high-pressure media, creating a textured finish that adds to the beauty of the application of materials such as metal, glass, stone, and wood. Although it may serve as a further means of enhancing surface appearance, it can have a few operational advantages, including promoting better surface adhesion for coating and higher wear resistance.
Incorporeal improvements brought by the development of media abrasive technology allow for an array of finishes to be imposed: from fine and matte textures to more obvious and tactile patterns. For instance, an extremely fine abrasive aluminum oxide can provide a detailed finish on a delicate material, whereas coarser media such as steel grit may provide heavy-duty industrial finishes. Studies suggest that sandblasted surfaces show enhanced reflectivity and optical properties and are well suited for contemporary architecture and design. At the same time, in commercial settings, these finishes increasingly mask surface imperfections and resist fingerprinting in conformity with current functional and design trends.
The very dynamism given to what is an otherwise commonplace finishing technique still makes sandblasted finishes an interesting variation on beauty and utility for designers, manufacturers, and consumers.
Applications of Sandblasted Stainless Steel

- Architectural Design
Sandblasted stainless steel is often found in building facades, interior panels, and decorative accents. It diffuses light to create the modern matte finish in smooth contemporary architectural manifestations by masking imperfections. According to the studies carried out, in facades, the ambience of low glare is created for the urban environment while retaining the utmost corrosion resistance, especially against pollution or sea air.
- Consumer Products
It is famous among household appliances (refrigerators, ovens, dishwashers), since the sandblasted surface achieves the most elegant appearance. This matte surface resists any fingerprint or smudge that may come its way and hence is suitable for products undergoing heavy handling. Studies indicate that among sandblasted appliances, visible surface marks tend to be 45% fewer when compared against polished ones.
- Medical and Laboratory Equipment
Such a nonporous and hygienic surface is more suitable for surgical instruments, laboratory workstations, and medical apparatus. All sandblasted finishing processes allow sterilization and resist bacterial proliferation with data showing that these finishes meet stringent hygiene requirements as set by governing agencies, including ISO and FDA certifications.
- Food and Beverage Industry
Sandblasted stainless steel is extensively employed in food processing machinery, kitchen countertops, and storage containers to guarantee safety and durability in constant exposure to moisture and high temperatures. Its non-reflective surfaces help in reducing operators’ visual fatigue in processing environments, whereas the abrasion resistance offers 20% additional service life to the equipment, as claimed by industry surveys.
- Transportation Sector
Sandblasted stainless steel finishes are utilized to manufacture interiors for trains and automotive and aerospace trim. Its ability to endure high stress, temperature fluctuations, and mechanical wear makes this a favoured choice in highly demanding transportation environments. Also, these sandblasted finishes reduce light reflections; hence, they improve aesthetics for passengers and also ensure safety.
- Industrial Equipment
Use in Architecture and Facade Design
In a modern architectural style, sandblasted stainless steel is preferred for its unique set of specifiers; durability gives it an aesthetic flexibility and environmental resistance finish from matte branding with glazes that create a sharp, contemporary look, especially when applied on facade claddings, interior wall panels, and decorative features. The material is adequately capable of resisting urban pollutants, coastal saltwater environments, and temperature changes along with regional weather guarantees for minimal deterioration over time.
In the last few decades, manufacturing processes have developed to hold sandblasted stainless steel as a possible member of the sustainable building design, the high recyclability of the material enabling a greener approach to reduce environmental impact and thus fulfill the requirements of green building certificates like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design). Plus, it is complementary with other materials like glass and stone to create implied contrasts that hover on both enhanced structural strength and visual identity of an architectural project.
Applications in Kitchen Equipment
- Countertops and Worktops: Due to its non-porosity that prevents surface bacteria accumulation, sandblasted stainless steel is an excellent choice for kitchen countertops, commercial or home. It is also critiqued for its resistance to heavy usage and for not fading with use over time.
- Sinks: Stainless steel sinks take advantage of this cleanroom-grade surface for corrosion resistance and easy cleaning throughout the cleaning and maintenance phases in professional and industrial kitchens.
- Cookware: A sandblasted stainless steel pot, pan, or cookware allows even heat distribution and offers resistance to warping. Also, these surfaces are suitable for induction cooktops.
- Cooking Appliances: Sandblasted steel has found its way into ovens, stovetops, and grills for heat resistance and that refined, professional look.
- Refrigeration Units: Stainless steel finish sandblastings are used for the exteriors and interiors of refrigerators and freezers because of the very advantageous thermal insulation property, alongside the custom of being corrosion-resistant.
- Food Preparation Tools: These include knives, spatulas, and mixing bowls that combine the ease in cleaning and durability when in constant heavy use.
Statistics show that in over 70% of professional kitchens across the globe, stainless steel components are used, with sandblasted finishes gaining popularity as they can hide scratches and fingerprints, keeping the appearance clean and polished. This very trend goes on to demonstrate the importance of sandblasted stainless steel in satisfying the entire gamut of functionality and aesthetics required in modern-day kitchens.
Maintenance of Sandblasted Stainless Steel

In cleaning and maintaining a sandblasted stainless steel surface, one should retain gentle care with mild detergents that do not contain abrasive substances; in other words, warm soapy water will do. Use a soft cloth or sponge for washing to retain the surface’s original texture. One should rinse off with copious clean water, then dry away using a lint-free cloth that can prevent watermarks. For harder stains, mixtures of diluted vinegar or commercial stainless steel cleaners could come into play. Avoid the use of strong chemicals or abrasives, such as steel wool. They will engrave scratches on the surface and ruin its finish. Builders are increasingly working towards this routine to ensure the material sustains its endurance and appearance over the long term.
Tips for Preserving the Sandblasted Finish
- Use Gentle Cleaning Solutions
Regular cleaning should be carried out with mild pH-neutral soap combined with warm water, preventing dirt buildup and possible contamination of the sandblasted texture. Practical studies revealed that the use of pH-neutral cleaners prevents surface deterioration, thus providing less opportunity for surface breakdown during long-term use.
- Apply Protective Coatings
To further protect the sandblasted finish, sanction the application of a clear protective sealant. This patent effectively blocks moisture, dirt, and grime from possibly wearing down or discoloring the surface in the future. Silicon-based penetrating sealants and similar products will significantly enhance protection capabilities while maintaining the original matte appearance.
- Minimize Abrasive Contact
Scrubbing pads, wire brushes, or abrasive cleaning materials should never be used, as they will erase the uniformity inherent on the sandblasted surface. Empirical tests have shown that abrasive instruments increase surface wear to an incidence rate of 30% when compared with the usage of soft microfiber cloths.
- Prevent Corrosion Through Proper Drainage
Water should never stagnate on surfaces when installed outdoors. Inadequate drainage will lead to water staining or mineral deposits on the sandblasted finish. Such issues can easily be circumvented through the use of a sloped setup and a sufficient drainage system.
- Perform Periodic Inspections
Scheduled maintenance should include inspections to keep watch for wear, discoloration, or any localized damage. Preventing major damage begins with treating minor problems, like small stains or scratches. Industry observation recommends carrying out inspections twice a year at the very least for surfaces exposed to environmental stresses.
- Protect Against Harsh Environments
Cleaning Techniques to Avoid Damage
While maintaining sandblasted surfaces, it is important to prevent any harm to the material during the cleaning process. Never use abrasive cleaning pads or steel wool as they might actually cause new surface imperfections or wear on the surface. Use nonabrasive microfiber cloths or soft brushes designed specifically for delicate surfaces as substitutes. Very High-pressure washers should also be considered unsafe and prohibited since they might cause erosion to the sandblasted texture, thereby abating its effectiveness with time.
Choosing the Right Finishing Technique

The selection of a finishing method will depend on the kind of material under consideration, its appearance, and its functional properties. A metallic surface may be viewed upon to be done with sandblasting, electroplating, or powder coating with finishes meant to last for durability and give an aesthetic value. Non-metallic surfaces, such as those on wood or plastic, would favor staining, polishing, or protective clear coatings. When selecting, keep in mind a finish that will hold up to wear and environmental exposure in the long run, as well as your specific operational requirements. Industry-specific standards can aid in making a decision, but testing small samples will also verify compatibility and effectiveness.
Comparative Analysis of Finishing Techniques
|
Finishing Technique |
Key Advantages |
Key Disadvantages |
Typical Applications |
Durability Level |
Cost Implication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Anodizing |
Corrosion-resistant, enhances durability |
Limited to aluminum materials |
Aerospace, architecture |
High |
Moderate |
|
Electroplating |
Decorative, wear and corrosion resistance |
Can flake or peel over time |
Automotive, electronics |
Moderate to High |
High |
|
Powder Coating |
Uniform finish, eco-friendly process |
Difficult to repair touch-ups |
Automotive, appliances |
High |
Moderate |
|
Polishing |
Improves aesthetics and smoothness |
No significant corrosion protection |
Jewelry, decorative items |
Low |
Low |
|
Staining |
Highlights natural appearance of materials |
Vulnerable to environmental changes |
Furniture, wood paneling |
Moderate |
Low |
|
Clear Coating |
Transparent protection, enhances longevity |
Can yellow or degrade over time |
Wood, metals, coatings |
Moderate to High |
Moderate |
|
Galvanizing |
Cost-effective corrosion resistance |
Adds weight, limited color options |
Construction, outdoors |
Very High |
Moderate to High |
Consulting Professionals for Best Practices
Recent and continuous findings are essential when deciding on the most suitable material finishes and protective treatments. This is an area where professional advice can be crucial. Such service providers are well-experienced in considering all the requirements of a specific project, among other things, environmental conditions, material compatibilities, and intended durability. For instance, understanding when it is practical to galvanize as opposed to powder-coat will vastly increase the lifespan of any outdoor steel works. Professional inputs will also assist in the uptake of newer technologies, such as nanocoatings that vastly outperform traditional coatings in abrasion and environmental damage. Combining expert advice with current research and practical evaluation can enhance the performance of project outcomes and sustain them for the long term, especially according to relevant applications.
Practical Advice for Selecting Finishes
The past few years have witnessed the start of the market favor for nano-engineered finishes in locations for which heightened abrasion resistance and easy maintenance are necessary, according to industry reports published recently. The purpose of these finishes is to create a molecular-scale barrier able to reduce surface wear and hamper dirt or contaminant build-up. Also, keep in mind that this finish’s lifecycle costs consider not just upfront applications but maintenance requirements over time.
Reference Sources
-
Study of Corrosion Behavior in Food Industry Applications
- Source: PMC
- Summary: This research focused on AISI 304L stainless steel, widely used in food processing due to its corrosion resistance. It evaluated the effects of surface treatments like sandblasting and passivation on corrosion resistance. Findings revealed that sandblasting increased surface roughness, reducing corrosion resistance, while passivation improved durability by enhancing the protective oxide layer.
-
Electrodeposition of Copper Coatings on Sandblasted Stainless Steel
- Source: MDPI
- Summary: This study developed a novel computer vision method to analyze copper coatings on sandblasted 304 stainless steel. The coatings were applied using electrodeposition, and the method assessed surface uniformity and coating quality.
-
Impact of Sandblasting on Corrosion Behavior of Carbon Steel
- Source: ScienceDirect
- Summary: This investigation examined how sandblasting time affected the corrosion resistance of carbon steel in various pH environments. Sandblasting improved corrosion resistance in alkaline solutions but increased corrosion activity in acidic and neutral solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is sandblasted stainless steel and how is it made?
A: Sandblasted stainless steel refers to stainless steel that has undergone a sandblasting process, where abrasive particles like glass beads or aluminum oxide are propelled at high velocity to create a unique surface texture. This technique not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the stainless steel but also prepares its surface for better adhesion if a protective coating is to be applied. The process involves using an air compressor and a nozzle to direct the abrasive material onto the stainless steel sheet or plate. The result is a matte finish that can effectively remove surface contaminants and blemishes, making it ideal for decorative purposes in interior design or kitchen equipment.
Q: How does sandblasting affect the corrosion resistance of stainless steel?
A: Sandblasting stainless steel can enhance its corrosion resistance by removing surface contaminants that may lead to rust or oxidation. When the surface is properly treated, it allows for better adhesion of protective coatings, which can further prevent corrosion. The blasting process also helps in creating a uniform surface finish that can resist environmental factors more effectively. However, it is essential to note that the type of abrasive used can impact the stainless steel surface; for instance, using silicon carbide might yield different results compared to steel shot. Proper surface preparation is crucial for achieving optimal corrosion resistance.
Q: Can sandblasted stainless steel be used for kitchen equipment?
A: Yes, sandblasted stainless steel is commonly used for kitchen equipment due to its durability and corrosion resistance. The sandblasting process not only removes any surface imperfections but also creates a finish that is easier to clean, making it suitable for food preparation areas. The unique surface texture can help hide fingerprints and other smudges, contributing to a more hygienic environment. Additionally, when using stainless steel plate for kitchen applications, the sandblasted finish can enhance the overall aesthetic appeal, making it a popular choice for modern interior design.
Q: What are the advantages of using a sandblasted finish sheet for decorative purposes?
A: A sandblasted finish sheet provides several advantages for decorative purposes, including a unique surface texture that adds depth and interest to various applications. This type of finish can create a matte look that is visually appealing and less prone to showing fingerprints or dirt. Furthermore, using sandblasted stainless steel allows for customization in design, as it can be tailored to fit specific aesthetic requirements. The corrosion resistance of stainless steel is maintained, ensuring longevity even in demanding environments. Whether for architectural facades or interior design elements, a sandblasted finish sheet is both practical and stylish.
Q: What type of abrasive is best for sandblasting stainless steel?
A: The best type of abrasive for sandblasting stainless steel largely depends on the desired finish and the specific application requirements. Common abrasives include glass beads, aluminum oxide, and silicon carbide, each giving different surface textures and finishes. For example, glass beads are often used for a softer matte finish, while aluminum oxide provides a more aggressive etch and is suitable for heavy-duty cleaning. It’s critical to select an abrasive that won’t damage the stainless steel surface while still being effective in removing contaminants. Best practices suggest testing different abrasives to determine which yields the best results for your particular project.