When considering the most viable options and the best techniques, there is an aspect of perspective that surrounds the uses of a microwave oven not only in the general population but also in the clinical setting. Although these innovations simplify our lives, hasten many activities, and broadly improve our lifestyle, they can also have detrimental effects on our physical health if minute precautions are not taken. In the case of the new microwaveable safe cooking and storage ware, the question comes down to “whether or not it is safe to microwave food in a Tupperware?” Can I microwave plastic containers? It’s true that plenty of individuals possess a microwave but use it very seldom; if not, they are still stuck in a traditional method of heating food or refrigerating their beverages. On the flip side, there are lovers of technology, yet they often get incapacitated because they don’t know how to troubleshoot some of their devices. In all the above situations, microwaving in plastic is usually a court-struck tensioner’s effect, right?” Ask about my lover’s situation without considering their respective personalities. Whether my wife or any man would want to answer some questions, the fact remains the same – there is a barrier that makes such questions uncomfortable to ask in real-life situations.
Introduction to Microwaving Stainless Steel
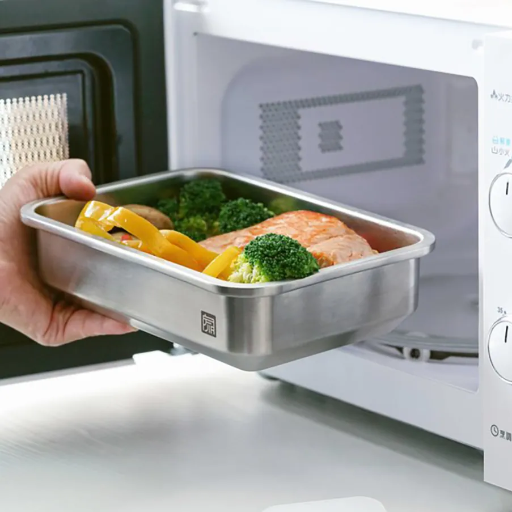

The no-brainer answer is not really, you don’t have to insert stainless steel when using a microwave. The no-brainer answer is, empirically, stainless steel does not work with microwaves. Stainless steel does not absorb microwave energy; instead, it bounces it back to the source which is not a good thing. This may cause undercooked or unevenly hot meals. Even worse, this wave can be destructive to the microwave itself; this can render the microwave inoperable due to the occurrence of fire or irreparable damage. Microwave ovens restrict the metals that can be utilized inside, and other metals, such as steel, do not meet the requirements; Therefore, is not safe for use in microwaves. Maintaining the proper function of your microwave cookware, which includes glass, ceramics, and heat-safe plastics that can be used in the microwave, is ideal. Finally, always refer to the user guide to understand what materials are recommended for use on your microwave when you fail to find an appropriate material applicable for use in cooking in a microwave.
Why the Question of Microwaving Stainless Steel is Common
The issue of microwaving stainless steel is indeed a pressing but often confusing one. This is mainly as a result of safe contradictory rules regarding its usage. At one end, it is well known that stainless steel is a hard, thermally stable material which is often used in the preparation of utensils and cookware, thus creating a misconception about its potential safety when placed in a microwave. The other school of thought is that there are reports of misadventures causing sparks, arcing and possible explosions of the oven when certain metals are placed inside. Some electronic home appliances and storage units for food that have been marketed of late contain metal materials that are microwave safe, so they get this mixed up about the smaller confines of regular metal in microwaves. It becomes even more confusing, which even contradicts such theories about stainless steel, due to different advice by different manufacturers and against the use of any metal in microwave by many. Such persons normally prefer recourse to official information, seeking the use of manuals and some scientific institutions to get correct propaganda on this particular question.
Relevance of Safe Kitchen Practices
Healthy and environmentally friendly kitchen habits are key to health and welfare of all people, not just those dealing with food crafts. They include but are not restricted to proper food storage, hygiene measures, and the appropriate implementation of kitchen utensils and equipment. The more recent examination of healthy kitchen behavior, for example, revealed the issue of cross-contamination, specifically among foods such as meat, which can also be contaminated. If cross-contamination occurs, bacteria, especially harmful ones such as Salmonella and E. coli, can transfer from raw to non-raw surfaces, secondary food-contaminated utensils, and foods. It includes food prepping and consumption, and in such cases where microwaves and other products are used, it is also crucial to be informed and alert about using such products as they may result in thermal burns, or have risks of improper materials like metal. Ensuring that the latest data, especially how to socialize in a healthy and safe way, affects not to take chances and make appropriate prescriptions of what we need ot do to survive nutritionally.
Overview of Stainless Steel in Food Storage
Stainless steel is heralded for its durability, safety, and functionality; it is used extensively in food applications. The corrosion resistance of stainless steel is achieved due to the presence primarily of iron, chromium, and other alloying elements, and the ability to form a thin protective film of chromium oxide when interacting with the ambient atmosphere. This is good because, even if food is stored for a long time and stored in acidic and highly humid areas, they do not get contaminated. Also, as opposed to plastics, it is stainless steel and containers made from this material, which have zero harmful chemicals to the food or preserve food smells, making it suitable for a longer duration of usage. It helps correctly store food without worry.
How Microwaves Interact with Stainless Steel?

Stainless steel behaves as a conductor when exposed to microwave radiation. The behavior for a given piece of stainless steel would, however, need to be described qualitatively for a particular shape and thickness. More specifically, if a piece of stainless steel is made in a certain shape and placed in a microwave, it would be a perfect reflector because waves are either reflected from the steel or are absorbed by it but are not transmitted through. For this reason, you cannot put this substance in a microwave and heat it properly, irrespective of how long you leave it in. Over and above that, in case of stainless steel with sharp edges or thin, it can undergo arcing or generation of electric sparks, which can damage the oven or even cause danger to the user. To suit the needs of consumers, molded microwave-safe stainless steel containers capable of preventing such issues are now available. Therefore, it is always best to check the technical specifications published by the maker so as not to allow stainless steel to bond during use in a microwave oven.
Materials and Their Interaction with Microwaves
How a substance responds to microwave energy depends on its constitution, particularly the dielectric properties. Essentially, dielectric properties decide how well the loose or bonded current carriers, i.e., dipoles, can convert the alternating current field into heat. Since the dipolar moment, instead of a three-dimensional structure, is active, dielectrics of the more aggressive liquid type, like water, are far more efficient; they are said to have higher dielectric conditioning. They are known popularly as polar liquids but this even goes for certain foodstuffs, which contain naturally occuring compounds that possess an appreciable dielectric constant. In comparison with heating non-polar materials, which do not have this effect, microwaves do a pretty impressive job of heating any item that is rich in water due to these types of substances.
However, there are certain materials, including metals, which are not suitable for food heating in a microwave oven because they reflect these waves away, making them likely to burn the oven. In the case of metals, they work by establishing a distribution of electric currents on their surfaces; when microwaves are directed onto such a material, there is an electric surge in the form of sparks. Additionally, some ceramic and glass materials do not have an appreciable interaction with microwaves, hence making them suitable microwave sorters provided that they do not have high concentrations of metal oxides or any other conductive surfacing materials.
The newest material science improvements have concentrated on coming up with microwave-transparent coatings and polymers that are able to enhance the distribution of energy without any obstructions or reflections. Such innovations maximize safety and productivity in almost all microwave-based activities, including heating food and both large and small-scale industries. When the engineer understands well the molecular level of a material, then the engineer knows well what to fix in the microwave-based processes with a promise of better performance and reliability.
Understanding Stainless Steel in Microwaves
Arguably, most pieces of rationalization and evaluation in real life can be attributed to the current applause of stainless steel for its tensile strength, impermeability to corrosion, and stability in high temperatures, and its wide application in industrial backgrounds and homes too. Yet, microwaves still present their own interaction, which is very sophisticated, camouflaging electromagnetic theory and material characteristics with regard to stainless steel. The microwave waves thus do not get absorbed in the body of the metal but are partly or entirely reflected by the same. This is because there are induced electric currents on the metal when it happens to stainless steel. These electric currents, in the absence of correct engineering measures such as the correct shape, size, and location of the microwave reflector, have a tendency to stress the stainless steel plate by localised disruption due to the formation of plasma on the surface of the plate.
While it is generally not suitable for standard microwave use, improvements in construction, including new materials and coating techniques, enable stainless steel’s utilization when such enhancement is required. For example, such materials as stainless steel with specific coatings that allow microwaves to pass through them and help prevent such reflections are more useful in the relevant areas. Furthermore, the changes in design and materials and in the edge smoothing of structures reduce the likelihood of the effect of the mechanical arching, making the entire process of using such components in microwave technology more consumable.
Potential Risks and Safety Considerations

In microwave engineering the use of stainless steel elements requires rigorous health and safety control measures mainly due to the following reasons:
- Material Compatibility: There are other risks associated with the use of stainless steel in microwave systems. Among others, stainless steel can lead to a microwave heating at a particular place within a microwave regime. This, if not properly addressed causes energy imbalance and could make the system to be destroyed.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): In some implementations improper use of stainless steel can create improper electromagnetic shielding causing EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) however this may lead to system failure or may endanger other neighboring equipment.
- Thermal Stress and Deformation: Stainless steel cannot withstand high magnitudes of microwave energy. As soon as it gets exposed to energy, the steel undergoes thermal expansion al stress which is a cup of origin of flexural loads. As a result the steel tends to regenerate its components, which possess strength as correspondingly reducing the load of bending stress.
- Corrosion Resistance: On its own stainless steel is virtually corrosion-free. Nonetheless, obvious situations where corrosive response has occurred may be seen. Over time, some materials or surfaces may reveal a noncorrosive mechanism because the corrosion merely increased their corrosive resistance, which increases their risk of failure.
Precision engineering and stringent compliance with the set industry safety standards are essential when utilizing stainless steel in microwave applications. Inclusion of the material in the systems brings about the need for thorough testing and adherence to basic standards of safety. Furthermore, regular monitoring of the system’s performance climate contributes to further improvement in the stability of the systems available in the long run.
Hazards of Using Stainless Steel in a Microwave
Having a case in a microwave with stainless steel causes the electromagnetic heating waves to be distorted ultimately by exhibiting dangerous attributes. Remember that the nature of the material is that since it scatters the microwave energy, electrical arcing or sparks (caused by lattice defects) will appear. Arcing is known to spontaneously occur on the areas where there is concentration, most especially at the edge or a thin part of the metal where waves converge at a certain point thus creating a hotspot that can lead to a fire. Alternatively, the surface’s quality is such that it does not allow the energy in the waves to pass through it effectively which can result in poor or no cooking of the desired food or drink when microwaves are used.
One of the key factors that increases the dangerous nature of microwave use is the overexposure to the electromagnetic waves produced by the microwave magnetron. Everything, including the metallic finish of the microwave, stainless steel in particular, is also placed within a risk area because overheating can harm the magnetron and result in additional costs. Furthermore, some thin articles made of stainless steel, such as forks, and other cutlery, are liable to cause sparking, which can affect both the apparatus and typical materials in the vicinity of it. Hence, the risk to both the material and the safety of users by hazards that can be avoided has to be addressed by the consumer through the use of this specific equipment as instructed and accompanied by the safety precautions.
Possible Damage to the Microwave Oven
When a microwave oven is used improperly for a long time (for example, without a cover and putting in items that could not withstand heating), the microwave’s inner electrical parts are subjected to a lot of pressure. Among all the components, the diode is the one which is reported to be the most fragile as it is used to transform the power running into the magnetron to a higher voltage. The potential outcome is that the diode gets overheated and burns out, ultimately disabling the microwave oven until the malfunctioning part is replaced. Another thing is that continuous extensive heating may lead to the formation of weak spots in the capacitor which regulates the output voltage supplied. One by one, such faults will undermine the effectiveness of the electronic parts and raise questions about their reparability.
It is the repeated occurrence of fast moving elements or arcing in the interaction zone which can, to a certain extent, exacerbate the situation. It is such a structure that guides the electromagnetic waves coming out of the magnetron into the food preparation cavity, which is most prone to degradation. If the waveguide cover becomes burnt through or damaged in any other way, the microwave might cease to be a safe product by failing to prevent leakage. Keeping in mind that that is bad for the microwave itself. It is not only the appliance that such actions may compromise, but the owners as well. Protection and precautions, such as ensuring the smooth operation of the appliance and using it as indicated, are crucial in minimizing the risks.
Common Myths and Misconceptions

It is a prominent fallacy that persons can acquire malignant growths from some electrical gadgets, like microwaves which are mostly found in the kitchen. It is more likely that they confuse the hazards of probable perturbations in cells from ionizing radiation, like X-rays and gamma rays, as opposed to microwave energy. Microwave ovens emit non-ionizing radiation which contradicts known radiobiological principles of genetic and chromosomal mutation after irradiation. The microwave cooking oven is equipped with all the necessary accessories, including a safety lock that prevents the waves from escaping into the environment. According to the World Health Organization and the Food and Drug Administration of the United States, microwave ovens are safe for everyday use, so long as their doors are in working order and they are operated according to the manufacturer’s directions.
Debunking the Myth of All Metals in Microwaves
People often mistakenly believe that it is dangerous to use any type of metal within a microwave oven, either because it can spark or cause a fire. There is some basis for such a fear, since in some cases, specific types of metals, such as twisted or crumpled aluminum foil or anything that has pointed and cornered edges, can cause sparks due to intense electric current build-up at the sharp tips. Nevertheless, not all items made of which are capable of this. In all fairness, a variety of metal objects with a microwave oven can be safely used within limits. In fact, such methods were probably considered when creating microwaves that can support safe operation with metals. A few metallic pieces can be used, such as the extended buttons found in most microwave appliances in the market.
On another note, there are particular microwave ovens which come built-in with metal grates or shelves meant to be used without any problems. Most of these grills are over racks, which come coated to prevent arcing and do not re-radiate, particularly inside the microwave oven. The amount and design of the implemented metal also appears to be important. A metal surface that is typically smooth, flat with no cutting or sharp corners contains much less risk as it usually reflects rather than focusing the microwave energy. It is important to adhere strictly to the safety concerns raised by the metallic components that the manufacturers of individual microwaves may provide.
When Stainless Steel May Be Appropriate
There are some circumstances in which stainless steel components can be located in a microwave, but only in the most modern types designed for such use. These ovens are provided with state-of-the-art technology, which addresses electromagnetic interference that arises when metals are used in such buildings; this prevents issues such as arcing or concentration of energy. For example, the metal produced with a smooth surface such as stainless steel has an upper limit of being more secure than materials with sharp angles and corners in such a place. A type of research on the arrangement of kitchen equipment has shown that some microwave ovens have a stainless steel lining to help with improving heat yield in convectional cooking while benefiting from heat reflection effects. Of course, all this ingenuity works only as it is intended by the manufacturer, and it is very important for buyers to understand that all the provisions of the user guide, as well as the particular specifics indicated, must be followed. Such adherence should be given top priority since the result of any slight deviation may greatly reduce the efficiency of the product and or endanger the safety of the user.
Clarifying Microwave-Safe vs. Non-Microwave-Safe Containers
|
Key Point |
Explanation |
|---|---|
|
Plastic containers |
Use microwave-safe plastic; avoid non-labeled or cracked items. |
|
Glassware |
Only heat-tempered, microwave-safe glass containers are recommended. |
|
Ceramic dishes |
Use labeled “microwave-safe”; avoid those with metallic accents. |
|
Paper products |
Ensure only microwave-approved paper, free of coatings or inks, is used. |
|
Metal containers |
Do not use; may cause sparks or damage to the appliance. |
|
Aluminum foil |
Use sparingly; ensure it does not touch microwave walls. |
|
Silicone containers |
Ensure they are microwave-safe; avoid over-heating or deforming them. |
|
Styrofoam |
Use only microwave-labeled types; others can melt and release chemicals. |
|
Plastic wrap |
Use only microwave-safe wraps; leave a vent for steam. |
|
Dishware with gold/silver trims |
Avoid completely; metallic trims create sparks and overheating risks. |
|
Recycled materials |
Avoid as they may contain unknown substances unsafe for microwaving. |
|
Food packaging |
Check labeling; some pre-packaged meals include microwave-safe instructions. |
|
Sealable containers |
Vent the lid to prevent pressure buildup while heating. |
Practical Tips for Using Stainless Steel in the Kitchen

- Proper Cleaning
To properly take care of stainless steel, particularly its austenitic variety, we have at hand, feel free to use only clean warm water, a few drops of liquid soap, and a soft sponge to avoid damaging. Remove exemplary strong dirt by mixing a bit of sulphate with water.
- Preventing Stains and Discoloration
Attempt to make sure that the stainless steel is never left to dry in air following the water cleaning procedure. For the cleaning cloth, it should be a micro-fiber cloth in order to keep its neatness. One should avoid using stainless steel in contact with extremely acidic or salty foods since they tend to discolor the surface of the stainless steel.
- Cooking Safety
Be cautious when using low heat when cooking food in stainless steel cookware. Overheating causes strains on the surface hence discoloration or damage to the pan. Furthermore, when you cook food in stainless steel, make sure that you warm the pan first before adding oil or the food to avoid sticking.
- Avoiding Damage
Also, avoid using stainless steel tools on non-stick surfaces and do not cut food directly on a stainless steel pot or pan. This has a cowardly effect on the slink of the heart. And many cooking options become less of an option once you have stuck a utensil on a wire mesh.
- Maintaining Longevity
You need to periodically check if there are any damaged or missing parts to the cookware. Please, as mixins, as well as you can prevent the finger marks and stained areas that may be left on the stainless steel materials by rubbing it with vinegar and water, mixing thoroughly, and cleaning it with a clean stainless steel cleaner periodically..
How to Avoid Issues When Microwaving
Best Practices for Stainless Steel Food Containers
Using stainless steel food containers is again a tough and eco-friendly, well-made food storage alternative strategy. However, the very important issue in its services, as well as longevity, is maintenance. First of all, when using the container, it must be a stainless steel food container for food that is proportionate to the cost of the container and designed for storage of food and has been certified to act as a food container to avoid any contamination. When storing acidic or salty foods, use containers labeled as non-reactive to prevent chemical reactions that could alter the taste or quality of the food. This is because steel can create sparks and so any food should not be warmed in this kind of container because of the effect their use has in reheating of food.
If you are going to wash plastic food storage of any sort, it is recommended to hand-wash with warm, soapy water since stains and odors can build up. However, most containers can also go in the dishwasher. Do not use any abrasive or sharp cleaners as they may scratch the surface, and scratches hold bacteria and impair the surface’s physical properties. In order to eliminate smells, it is advised to dry the containers properly or use fresh hand for drying the containers after washing.
Reference Sources
-
Microwave Pyrolysis of Plastic
- Key Findings: This study explored the interaction of microwave energy with stainless steel thermocouple sheets. It highlighted that stainless steel, being a poor conductor of heat and current, affects the efficiency of microwave pyrolysis processes.
- Read more
-
Utilization of Steam Heat Generated via Microwave Energy in Seafood Cooking
- Key Findings: The study demonstrated the use of stainless steel microwave units for seafood cooking, emphasizing their ease of cleaning, sanitization, and reduced cooking times.
- Read more
-
Effect of Separator Thickness and Preheating Temperature on Microwave Processed Composite Clads
- Key Findings: This research focused on the development of composite clads on austenitic stainless steel substrates using microwave heating. It found that microwave cladding can effectively create durable composite layers.
- Read more
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Can You Microwave Stainless Steel Products?
A: Many people are hesitant about using stainless steel in the microwave due to concerns about safety and potential damage. Stainless steel products, especially those that are not labeled as microwave-safe, can cause problems when used in a microwave oven. If the item contains metal, it may create an arc, which can damage the microwave oven and pose a fire hazard. It is essential to ensure that any stainless steel container you use is specifically designed for microwave use. Today, it is easy to find microwave-safe stainless steel food containers that meet safety standards. Always check for labels indicating whether a particular stainless steel item is safe for microwaving.
Q: What Happens When You Put Metal in the Microwave?
A: When you put metal in the microwave, it can cause sparks and arcs due to the electrical currents that occur inside the microwave oven. This is particularly true for metal objects that are not specially designed for microwave use, such as regular stainless steel bowls or containers. If you use a piece of metal that is not microwave-safe, it can damage the interior walls of the microwave oven and potentially cause a fire. Therefore, it is best to avoid using any metal food containers unless they are labeled as microwave-safe. Always opt for high-quality microwave-safe containers to ensure safe heating of your food.
Q: Can You Use Microwave-Safe Stainless Steel Containers for Reheating?
A: Yes, you can use microwave-safe stainless steel containers for reheating food, provided they are specifically designed for that purpose. These containers are made of 304 grade stainless steel and have been tested to ensure they do not cause issues in microwave ovens due to electrical currents. Using high-quality stainless steel containers is an excellent option for reheating food without creating food waste. Always verify that the container is labeled ‘microwave safe’ before using it in the microwave. It is advisable to check for any specific instructions from the manufacturer to ensure safety during microwaving.
Q: How to Identify Microwave-Safe Containers Made of Stainless Steel?
A: Identifying microwave-safe containers made of stainless steel is crucial to avoid potential hazards. Look for containers that are clearly labeled as microwave-safe, which indicates they have been tested for use in microwave ovens. The British Stainless Steel Association also provides guidelines on which stainless steel products can be safely used in microwaves. Containers that are made of 304 grade stainless steel are generally considered safe, but it’s always best to double-check the manufacturer’s specifications. Additionally, new microwave-safe containers are now being sold on various platforms, ensuring easy access to safe options for reheating food. Always prioritize high-quality stainless steel options to guarantee safety and durability.