Because of the vandalism 4×8 sheet metal can undertake, 4×8 sheet metal is considered an essential raw material in any industry, including construction and auto manufacturing to small home-related DIY projects. You are either a professional or a curious enthusiast; in either case, knowing the basic factors like price, gauge, and use cases will help you make a good decision and squeeze the maximum yield from this common material. By the time you finish reading, you will have a complete understanding of how to analyze and apply 4×8 sheet metal to services that are meaningful to you.
What is 4×8 Sheet Metal?
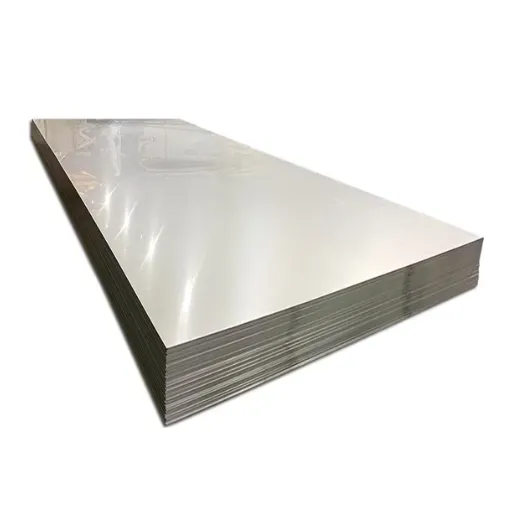

Common Materials Used
4×8 sheet metal comes in many materials commonly used, depending on the specific properties and applications required:
Steel
Steel is one of the most widely used materials for 4×8 sheet metal because of its strength, durability, and versatility. Carbon steel is especially popular with construction and industrial applications as it offers very good structural support. Meanwhile, galvanized steel is frequently chosen in outdoor-type projects or areas that tend to get wet as it is coated with zinc to prevent corrosion.
Aluminum
Being lightweight and naturally corrosion-resistant, aluminum is in high demand whenever the application needs weight reduction and resistance to environmental factors. It is widely used in the transportation, aerospace, and automobile industries and for roofing, siding, and ornamental usages. On top of that, because aluminum can be recycled multiple times, it is hence a green metal.
Stainless Steel
Since stainless steel is highly corrosion resistant and is thought to have a polished finish, it is used in the kitchen setup, medical instruments, and architecture whenever look and sanitation are considered. It is highly durable and resistant to rust and staining, so the environment is not harsh for it.
Key Insight: Each of these materials has its own downfalls and upsides, depending on the requirements of the project: strength, weight, corrosion resistance, and cost. Understanding the qualities of each material is therefore the only way to go about choosing the appropriate type of sheet metal for your needs.
Understanding Gauge and Its Importance
Gauge refers to the measurement standard of the thickness of the sheet. It influences the strength, weight, and flexibility of the material and these are the main requirements of applications. Lower gauge numbers indicate thicker sheet metal, while higher gauge numbers indicate thinner sheets. For example, a 10-gauge steel sheet is far thicker and stronger than a 20-gauge steel sheet. It is a measurement system for manufacturers and engineering so that material specifications are standardized and thereby consistent throughout a project.
Why Gauge Matters
- Thicker sheets (lower gauge) are heavy in applications where strength or durability is desired before it is rubbed hard by stress
- Higher-gauge sheets are preferred where the sheet must be light in weight and flexible, for example, in automotive panels or duct
- The gauge thickness is matched with the functional requirement of the projects so that it doesn’t compromise performance and remains cost-effective
The accurate selection of gauges also makes a smoother production process. Welding, bending, or forming directly depends on thickness. Taking the proper gauge allows handling of the operations efficiently without breaking the material integrity. It becomes therefore mandatory that any sheet metal worker must know how functionality is affected by gauge.
Types of 4×8 Sheet Metal

Galvanized Sheet Metal
Galvanized sheet metal is a kind of steel that is given a special zinc-coating process to resist corrosion and rust. Depending on the application, the protective coating may be set through a hot-dip process or could be electro-galvanization. This coating serves as an additional barrier against weathering conditions made of moisture, chemical Pollutions, etc. The end product is extremely durable and has a longer life as compared to uncoated steel sheets. The versatility of galvanized sheet metal makes it among the most preferred metals used in industrial, construction, and automotive fields.
Applications include: roof construction, HVAC ducting systems, panel siding, outdoor furniture, and agricultural equipment. Its capacity to withstand adverse environments assures excellent performance from the start while keeping the cost of ongoing maintenance lower.
The galvanized sheet metal comes in varying thicknesses and gauges; this is necessary to accommodate different project requirements. Designers and engineers must make a conscientious appraisal in selecting the gauge of the metal to obtain optimal performance at least cost, keeping the material subjected to the necessary loads without unnecessary weight and cost. With recent advances in coating technologies, other types of finishes may also be possible, including colored finishes or finishes with higher corrosion resistance. This opens up greater possibilities for its application in various industries.
Steel vs. Aluminum Sheets
While steel is denser, stronger, and cheaper, it is susceptible to corrosion; aluminum, on the other hand, is lighter, more resistant to corrosion, and costlier.
| Aspect | Steel | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Dense | Lightweight |
| Tensile | Higher | Flexible |
| Mass | Heavy | Light |
| Rusting | Susceptible | Resistant |
| Expense | Affordable | Pricier |
| Robustness | Durable | Moderate |
| Heat Transfer | Low | High |
| Magnetic | Yes | No |
| Joining | Simpler | Specialized |
Specialty Plates and Their Uses
Specialty plates are precision-engineered materials, customized to suit the particular application. With this general specification, certain characteristics were kept unique to suit some industry requirements. These plates undergo the finest metallurgical processes to make them achieve either an increase in tensile strength, corrosion resistance, or thermal stability. These plates are used for aerospace, automotive, and marine applications because of their favorable strength-to-weight ratios and their ability to endure aggressively corrosive environments.
HSLA Plates
High Strength Low Alloy plates provide superior mechanical properties together with improved weldability, widely used in heavy construction and transportation.
Heat-Treated Stainless
Used in food processing industry due to resistance against contamination and corrosion, essential for compliance with stringent hygiene standards.
Abrasion-Resistant Plates
Essential for mining machinery and applications dealing with heavy wear and tear, hardened surface while maintaining ductility.
Other aluminum specialty plates find unique application fields in aerospace and renewable energy industries. Owing to their potential light weight and indeed high thermal as well as electrical conductivities, these plates would be prioritized for aircraft components, mounting of solar power, and conductive busbars into power networks. And with some fabricated for temperature resistance and others for custom dimensions, the scope of specialty plates keeps on growing with new material sciences, responding to the call of performance optimization in industries.
Benefits of Using 4×8 Sheet Metal
Durability and Longevity
Due to its excellent durability and longevity, the 4×8-size sheet metal is sought after in several industrial classes. The resilience factor actually depended upon the physical properties of the material, coatings, and fabrication methods, all designed to make sure that the item stays undisturbed in an aggressive operational environment with prolonged utilization. Here are the five reasons for the durability and longevity of the 4×8 sheet metal:
-
1
Corrosion Resistance
Many types of 4×8 sheet metal offer excellent corrosion resistance, especially in environments exposed to moisture or chemical action. For example, stainless steel alloys with chromium content of at least 10.5% develop a thin, inert oxide layer, which prevents it from rusting and further oxidizing.
-
2
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Alloys of higher quality offer top strength, along with low weight. This helps to lessen structural strain while not allowing the material to give away to heavy and mechanical working stresses.
-
3
Protective Coatings
Galvanization and powder coatings provide surface protection from weather rip, scratch, and abrasion. Steel that is galvanized can last for about 50 years in most cases without needing much to be repaired or replaced.
-
4
Resistance to Thermal Expansion
A high-grade 4×8 sheet metal can withstand very high temperature swings without warping or cracking. Materials like aluminum have tailored thermal coefficients that make them suitable for cases where thermal stability is required.
-
5
Recyclable and Retention of Properties
Sheet metals and their general mechanical properties do not change with respect to the recycling. Cyclical usability is such that the material can be reprocessed and reused while maintaining its strength and durability through several applications.
Conclusion: All these factors put together make 4×8 sheet metal the material of choice for industrial, architectural, and engineering projects where long-lasting performance is targeted.
Cost-Effectiveness and Pricing
When evaluating 4×8 sheet metal, its cost-effectiveness and pricing are in a combination of factors. This makes for its propagation in different industries. Five factors that summarize various aspects of its economic and market orientation are given:
Material Availability
The availability of raw material, for example, steel and aluminum used in the making of 4×8 sheet metal, assures of an uninterrupted supply chain creating minimum bottlenecks in production; thus, prices are competitive.
Manufacturing Scalability
These large-scale production methods such as rolling and extrusion allow manufacturers to produce bulk amounts of 4×8 sheet metals implementations, achieving economies of scale in the process and lowering their cost per unit.
Long-term Performance
With inherent durability, the 4×8 sheet metal provides an excellent long-term performance that minimizes maintenance, narrowing down replacement costs over time, thus, lessening cash expenses for the user.
Recyclability Value
Recyclability gives an economic value to sheet metals like steel and aluminum. Recycling diminution on production costs chiefly because it is less energy-intensive than production from fresh raw materials.
Market Versatility
Because of high market demand for roofing, auto panels, and industrial equipment, and with low production volumes, the 4×8 sheet maintains its competitive price options in all these industries.
All these reasons highlight the cost-efficiency that 4×8 sheet metal presents, keeping its name as one of the preferred materials in construction and industrial use.
Versatility in Applications
In virtually all industries, the adaptability of 4×8 sheet metal speaks to its economic and functional value. The particular strength-to-weight ratio and ease-of-fabrication qualities make the material immensely versatile with real-world applications. Following are areas of applications where 4×8 sheet metal finds uses:
-
🏗️ Construction and Roofing
It is a worthwhile material for construction, roofing, cladding, and partition walls. It duly offers resistance to environmental elements, and hence, it can be said that it has green construction practices built into it.
-
🚗 Automobile Manufacturing
Automobile manufacturing is very dependent on sheet metal for vehicle body panels, chassis structures, and custom modifications, which make best usage of high strength-to-weight ratio.
-
✈️ Aerospace Industry
Due to sheet metals’ load and fatigue resistances, it is one of the primary materials used in making fuselage components and wings and also for engine casings.
-
⚙️ Industrial Equipments and Machines
In equipment housings, panels, and frameworks, sheet metal bestows structural strength yet is inexpensive to manufacture.
-
🏠 Home Appliances
A slew of household appliances-from refrigerators to washing machines and ovens-utilize sheet metal for strength, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal.
Each of these applications reinforces the material’s role in driving innovation and maintaining sustainability across industries, making it an integral component in modern engineering and design practices.
Applications of 4×8 Sheet Metal

Construction and Structural Uses
The sheet metal that is 4×8 serves a vital function in construction and structural applications, owing to its versatility, strength, and ability to respond to different needs. Its regular dimensions and properties lend itself to various project applications. Five key areas demonstrate how 4×8 sheet metal is used in construction:
🏠 Roofing and Siding
Used widely for roofing and siding, especially galvanized and aluminum types. Being light in weight and resistant to corrosion, it provides weatherproofing.
🏗️ Framing Structures
Used in steel building frames, including studs or beams. Given its tensile strength, it can carry significant weight in tall buildings.
💨 HVAC Systems
Most suitable material for ductwork, fittings, ducts, and vents for residential and commercial purposes promoting free air flow.
🏢 Cladding & Facades
Used in building cladding and facade design. Stainless and aluminum varieties provide sleek looks with energy efficiency.
🌉 Infrastructure
Used in reinforcement and external cladding of large infrastructure projects like bridges and overpasses.
Roofing and Exterior Applications
4×8 sheet metals with their strength, weather resistance, and adaptability to various architectural designs have found crucial applications in roofing and exterior works. Here are five commonly seen uses and their relevance to this field:
-
1
Roofing PanelsUsed for nearly all types of houses, 4×8 sheet metals resist weather conditions-whether heavy rains, snow, or blazing sun, and offer durability. They refute heat absorption while keeping energy-efficiency property, claiming studies allowing metal roof to bring down cooling costs by as much as 25%.
-
2
Wall Cladding and SidingUsed popularly for external wall cladding, this material protects an edifice from weather elements of wind and moisture. Through further surface finishing such as galvanization or a painted coating, the product seeks to improve corrosion resistance and provide aesthetic versatility to align with design requirements.
-
3
Gutters and DownspoutsGutters and downspouts demand 4×8 sheet metal for the efficient management of rainwater. Being lightweight and malleable, it enables ease of installation; the anti-corrosive coating on it offers protection and long-term performance even when subjected to seasonal rains.
-
4
Fascia and EavesThe sheet metal is implemented for the fascia boards and eaves to secure them from water damage due to which they otherwise hasten the life of the roof system; being highly formable, it becomes the ideal choice of material to achieve exact and tight installation around the roof edge.
-
5
Decorative Facades and AwningsThe sheet metal is often used for creating contemporary decorative facades and awnings; it offers strength to the design while it also has some aesthetic value. The more advanced methods of fabrication allow for giving the material a complex pattern and texture to satisfy both functional and architectural intents.
Key Takeaway: Such applications bring to light the essentiality of 4×8 sheet metal in roofing and exterior architectural designs, their capacity to meet structural requirements and enhance energy efficiency, meanwhile holding out for long-term reliability.
Purchasing 4×8 Sheet Metal

Factors Influencing Price
Various elements influence the pricing of 4×8 sheet metal, ranging from the properties of the material to market factors. One major determinant of price stays with the choice of metal. Aluminum, steel, and stainless steel each demand varying costs depending on their corrosion-resisting capability, strength, weight, etc. Also, the presence of finishes or coatings can raise the price-it could be galvanized or powder-coated-for these treatments add to the lifespan and aesthetics of the metal.
💰 Key Price Factors
- Material Type: Aluminum, steel, and stainless steel each have different base costs
- Gauge/Thickness: Thicker sheets require more raw materials, increasing costs
- Finishes & Coatings: Galvanized or powder-coated treatments add value
- Customization: Pre-cut sizes, perforations, or unusual textures raise costs
- Market Conditions: Supply chain disruptions and commodity prices affect final pricing
Sheet gauge or thickness stands out as another critical factor concerning price. Thicker sheets consume more raw materials and hence weigh more, thereby increasing costs during production and delivery. In addition, the further custom dimensions, whether pre-cut sizes or perforations or an unusual texture, may subsequently go on to raise the overall cost of the sheet. These customizations generally need special types of fabrication, the value of which is also calculated into the labor cost and ultimately the selling price.
Lastly, price changes can occur because raw material prices and demand go through variations. The prevailing conditions in the world markets will have a direct bearing on the final sheet metal price with respect to a supply chain disruption or change in commodity price. Steel price up, aluminum supply shortage down-an obvious price differential occurs. When I keep track of these factors, I can purchase more efficiently and choose themes that suit my particular needs in the project while at the same time managing the budget.
Tips for Selecting the Right Gauge
Choosing the correct sheet metal gauge is quite essential to provide the best performance, structural soundness, and cost efficiencies in your design. First, evaluate your own design requirements. For example, mechanical strength and durability might need thicker steel gauge numbers, such as 14 or 16, while lighter applications like ductwork or signs might only require 22 or 24 gauges.
📋 Evaluate Requirements
Mechanical strength and durability might need thicker gauge numbers (14-16), while lighter applications like ductwork may only require 22-24 gauges.
⚖️ Compare Materials
Steel tends to be stronger than aluminum at the same gauge, but aluminum offers better corrosion resistance and lighter weight.
🌤️ Consider Environment
For corrosive conditions or extreme temperatures, prioritize materials with appropriate coatings (galvanized steel, anodized aluminum).
💰 Balance Cost & Function
Don’t compromise application strength for short-term savings. Use gauge conversion charts and load calculators for optimal selection.
One also has to consider the metal’s nature since the strength is somewhat at variance with thickness for an assortment of metals. Steel, for example, tends to be stronger than aluminium at the same gauge. On the other hand, aluminium is more resistant to corrosion as compared with steel and is much lighter, so it stands better than steel in application realms such as aerospace or marine. Always compare with manufacturers’ specifications and standards for strength of a material (for example, tensile strength, yield strength) that correlate with the load or stress conditions that your design will face.
Environmental factors should also play a role in gauge selection. If the material will be in corrosive conditions or exposed to extreme temperatures, metals should be prioritized with the respective coating or treatment options (galvanized steel or anodized aluminum), and gauge should be considered to maintain structural performance.
Lastly, a compromise between cost and functionality should also be considered by invoking trends in material prices and availability. A slightly thinner gauge is a bad decision for short-term savings if it compromises application strength and lifetime. Gauge conversion charts and load calculators are handy tools that help accelerate this process, so technical and budgetary considerations are kept in balance.
References
- Determination of Profiled Sheet Metal Strength under Standard Testing Loads Using Nonlinear FEA
Published on IOPscience – This article discusses the strength analysis of steel sheets under standard testing loads. - Comparison of Technology of Forming the Sheet Metal by Numerical Simulations
Academic Paper – This paper explores the forming technologies for sheet metal, including high-strength steel. - Sheet Metal Handbook: How to Form and Shape Sheet Metal for Competition, Custom and Restoration Use
Technical Guide – A comprehensive guide on sheet metal forming and shaping. - Click here to read more.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
❓ What is 4×8 sheet metal usually used for?
4×8 sheet metal finds its common use in several fields such as construction, automotive manufacturing, and home improvement works. The standard size lends itself well to panel, roof, and custom fabrication construction.
📏 What are the measurements of a 4×8 sheet metal?
4×8 sheet metal means the metal sheet would measure 4 feet by 8 feet. This size gives ample surface area to cut down or shape smaller parts for various applications.
🔧 What kinds of materials exist in 4×8 sheet metal?
The four-by-eight sheet metals can be made of aluminum, steel, stainless steel, and copper. That is, depending on varying properties that are in each material and differing applications they serve.
💲 How much does 4×8 sheet metal cost?
Pricing for 4×8 sheets varies with the material employed, the thickness behind the metals, and finish of selection. Usually, aluminum sheets are priced higher than steel on account of their being light and corrosion resistant.
📐 Does 4×8 sheet metal come in different thicknesses?
Yes, 4×8 sheet metal does come in different thicknesses, generally from 22 gauge up to 16 gauge or even thicker. Thickness selection will be judged according to whatever your project requires.
🛒 Where can one buy 4×8 sheet metals?
Places to purchase from include local hardware stores, metal shops, and online portals. On price and quality, a comparison should be made before buying.
✂️ How does one cut 4×8 sheet metals?
One can cut 4×8 sheet metals by tin-snipping, using a jigsaw, or executing cuts with a plasma cutter. The choice of tool depends on the metal’s thickness and how complex the cutting operation will be.
🔨 Is 4×8 sheet metal easy to work with?
Generally, 4×8 sheet metals are easy to handle, especially if you consider doing it yourself. Nevertheless, a good set of tools and safety precautions need to be taken in order to make precise cuts and assure safety.
🎨 Can I paint or finish 4×8 sheet metal?
Absolutely! 4×8 sheet metal can be painted or finished for beautification and protection against corrosion. It is better to use a metal primer before applying the paint.
🌍 What would be the environmental considerations concerning the use of 4×8 sheet metal?
Recycling needs to be considered when using 4×8 sheet metal, particularly for any scrap material. Most metals are recyclable and this definitely will help reduce the waste and environmental impact, thereby realizing a sustainable form of construction.