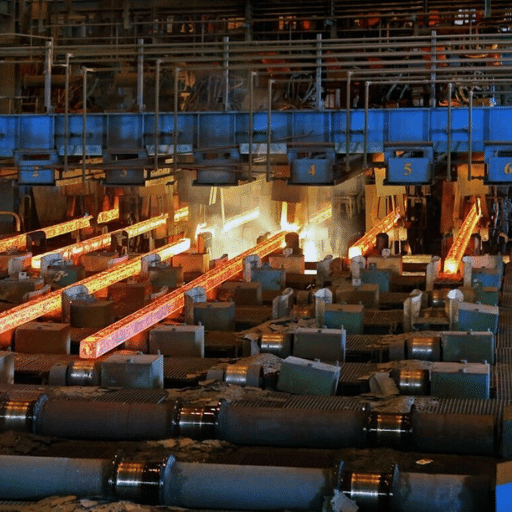
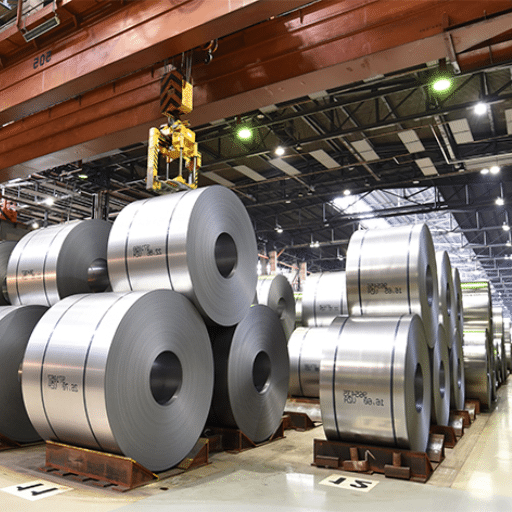
304 stainless steel coil is a versatile and widely used material that has become indispensable in various industries. Its remarkable strength, resistance to corrosion, and flexibility all contribute to the fact that this alloy is not only favored but also the best alternative for construction, automotive, food processing, and chemical sectors. This extensive article tackles the characteristics, uses, and specifications of 304 stainless steel coil and thus gives professionals and decision-makers an excellent platform for getting deep knowledge. If you are curious about its chemical makeup, performance traits, or applications per industry, this extensive guide will reveal to you why 304 stainless steel is one of the most important raw materials in present-day manufacturing and engineering contexts.
Understanding Stainless Steel

What is Stainless Steel?
Stainless steel is a metal that does not corrode easily and is mainly made of iron, nickel, chromium, and sometimes, in smaller amounts, of molybdenum and carbon. Its most remarkable property is that it can neither be oxidized nor corroded. This property comes from the fact that there is at least 10.5% chromium in the alloy. The chromium, through a chemical reaction with the oxygen in the air, produces a super thin layer of oxide, known as the “passive layer”, that is non-reactive and most of the time is not worn away. Therefore, corrosion cannot get through this barrier, and that is why steel keeps its strength even in very harsh environmental conditions.
Stainless Steel Categories
The different grades as well as finishes of the stainless steel allow its application across a wide variety of industries. The most important types of steels are austenitic, ferritic, martensitic, duplex, and precipitation-hardened, with each having its own distinct characteristics such as high or low strength, ductility, resistance to extreme temperatures, and ability to withstand a wide range of chemicals.
Stainless steel is utilized in almost every sector—building, car manufacturing, medical, food processing, and air travel—because of its easy cleaning, super strength-to-weight ratio, and durability. A recent study points to a rising trend in worldwide stainless steel production, which is attributed to the adoption of environmentally friendly production methods and the material’s ability to be recycled, thus being a significant factor in the development of industrial technology to come.
Introduction to 304 Stainless Steel
304 stainless steel is an austenitic grade and among the most preferred stainless steel alloys globally due to its fantastic combination of mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and versatility. The main ingredients are iron, chromium (18-20%), and nickel (8-10.5%) along with a few more like silicon and manganese. Its specific range gives it a great deal of resistance to oxidation and pitting depending on the nature of the corrosion and particularly with the case of mild corrosion, while it is still non-magnetic in the case of annealing.
| Property | Specification | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chromium Content | 18-20% | Excellent corrosion resistance |
| Nickel Content | 8-10.5% | Enhanced ductility and formability |
| Melting Point | 1400-1450°C (2552-2642°F) | High-temperature performance |
| Magnetic Properties | Non-magnetic when annealed | Suitable for sensitive applications |
Steel is easy to weld and shape, and so it is used in almost all industries like these: architecture, food processing, chemical equipment, and medical instruments. 304 stainless steel is predominantly used in the areas of cleanliness and hygiene because of its non-porous surface which makes it hard for bacteria to grow while being easy to wipe off.
📊 Market Insight
Newly emerged search pattern data reveals that the majority of queries regarding 304 stainless steel are associated with its resistance to very harsh environments (like marine or acidic) and comparisons with the 316 grade. This infers a growing interest in the material and a belief in its long-term reliability in different fields. In regular climatic conditions, 304 is still the most efficient and cost-effective choice but more extreme conditions may require top grades with better resistance features.
Comparison with Other Grades
The differences in composition and thus the different levels of resistance to corrosion are the main points to consider when comparing 304 stainless steel and 316. The consumption of stainless steel grade 304 in the industry is largely because of its excellent chemical composition of around 18% chromium and 8% nickel. But in case of working with environments that have a high level of chlorides, it is better to use 316 with the addition of molybdenum in the amount of about 2 to 3% more than 304.
304 Stainless Steel
- 18% chromium, 8% nickel
- Cost-effective solution
- Suitable for mild corrosive environments
- Excellent for indoor applications
- Ideal where extreme exposure is unlikely
316 Stainless Steel
- Includes 2-3% molybdenum
- Superior pitting and crevice corrosion resistance
- Best for chloride-heavy environments
- Higher initial material cost
- Reduces long-term repairs and replacements
Studies show that users are becoming more and more interested in the detailed differences between the grades and their economic viability and resistance to degradation in poor conditions. For instance, although 316 is more initially expensive, in scenarios with corrosive agents like salt or acid, the extra cost is often considered right since it leads to lower repair and replacement costs. Knowing these differences is very important in the choosing of the correct grade according to the specific operational requirements.
Specifications of 304 Stainless Steel Coil

Chemical Composition
The chemical composition of 304 stainless steel being the result of a careful and skilled work has produced a material with a set of properties that include very much corrosion resistant, good mechanical strength, and easy processing as well. According to the latest standards, the principal elements are around 18-20% chromium and 8-10.5% nickel. No doubt these chemicals are the main contributors for the very high resistance of the metal to corrosion and oxidation.
| Element | Composition (%) | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Chromium | 18-20% | Corrosion and oxidation resistance |
| Nickel | 8-10.5% | Corrosion resistance and ductility |
| Manganese | ≤2% | Improves strength and workability |
| Silicon | ≤1% | Enhances heat tolerance |
| Carbon | ≤0.08% | Maintains weldability |
| Phosphorus | ≤0.045% | Controlled for quality |
| Sulfur | ≤0.03% | Controlled for machinability |
Moreover, nitrogen in very small amounts may be added to 304 stainless steel as a measure to adjust the properties of the alloy. The skilled chemistry behind this makes 304 an alloy that offers great performance in various industries and commercial applications.
Mechanical Properties of Type 304
Stainless steel type 304 exhibits such an exceptional combination of mechanical characteristics that it is among the first in the list of candidates when it comes to the selection of stainless steel alloys for industrial applications. In general, its ultimate tensile strength is between 505 and 735 MPa, but it is dependent on heat treatment and the processing of the material. The yield point at 0.2% strain is about 215 MPa, which means that the material can be subjected to and carry moderate structural loads without becoming permanently deformed.
Key Mechanical Characteristics:
- Tensile Strength: 505-735 MPa (depending on processing)
- Yield Strength: ~215 MPa at 0.2% offset
- Elongation at Break: Approximately 40% (excellent ductility)
- Hardness: Brinell Hardness Number (BHN) 170-200
- Modulus of Elasticity: ~193 GPa (28,000 ksi)
- Temperature Range: Maintains properties from cryogenic to 870°C (1600°F) intermittent service
Type 304, in addition, exhibits an elongation at break of nearly 40%, which is a clear indication of its ductile nature and the capability to endure high tensile stress before fracture. The hardness of the alloy, reported as a Brinell Hardness Number (BHN) lying between 170 and 200, provides the guarantee of a combination of strength and resistance to wear.
✓ Performance Advantages
After all, Type 304 keeps its excellent combination of tensile and yield strength as well as its strength across a wide temperature range. Very low temperatures won’t affect its mechanical properties but it can only operate intermittently under 870°C (1600°F) because of its exceptional resistance to oxidation and thermal deformation. These mechanical properties, along with outstanding corrosion resistance, are the main reasons why Type 304 is considered the benchmark for stainless steel applications in the industry.
Thickness and Tolerances
Thickness and tolerances of Type 304 stainless steel are key factors that influence performance in all applications. Typically, standard sheet and plate thicknesses are from 0.25 mm (0.010 in) to more than 200 mm (7.87 in), and are made according to very demanding industry standards.
To determine such tolerances for given thicknesses, the parameters set in girths like ASTM A480 are taken, where the dimensional accuracy of stainless steel flat products is controlled. The tolerances guarantee evenness and strength of the product, which can cover the pickiest areas like the ones of a precision-fitted application in aerospace or medical industries, for instance, very strict tolerances that help to maintain uniformity all through the material manufacturing process.
Manufacturing Excellence
The modern manufacturing methods keep increasing the application of the most sophisticated quality control techniques in the thickness level control, where micro-level deviations are allowed. Newer revelations demonstrate that sticking to the set tolerances not only maximizes structural integrity but also cuts down on the waste of materials, thereby contributing to the current sustainability features.
Applications of 304 Stainless Steel Coil

Industrial Applications
The 304 stainless steel coil plays a key role in various industrial sectors due to its remarkable corrosion resistance, high strength, and excellent formability. Its versatility enables deployment across multiple demanding environments:
🏭 Chemical Processing
Primarily employed in production of tanks, pipes, and vessels for safe, long-lasting, and efficient handling of corrosive substances
🍽️ Food Processing
Non-reactive surface and hygienic characteristics make it perfect for storage tanks and conveyor systems
⚡ Power Generation
Especially in renewable sources like solar and wind power, where extreme weather resistance extends operational life
🏗️ Construction
Architectural applications requiring both aesthetic appeal and structural integrity
📈 Market Growth Projection
Recent data indicates that usage of 304 stainless steel coils is projected to rise at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of more than 5% from 2023 to 2030, positively impacted by worldwide growth in infrastructure and manufacturing industries. These diverse applications demonstrate the alloy’s quality and continued importance in today’s industrial progression.
Use in Heat Exchangers
One of the main reasons for extensive use of 304 stainless steel coils in heat exchangers is their superior corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, and mechanical strength. These material properties are extremely important for efficient operation and long service life of systems exposed to high temperatures and aggressive chemicals, including chemical processing plants, power generation facilities, and HVAC systems.
Industry Growth Data
The latest statistics suggest that the worldwide heat exchanger market demand will increase by a robust CAGR of 6.1% for the period from 2023 to 2030. The growth won’t be the only outcome of this trend, but also that the demand for versatile materials such as 304 stainless steel will continue to rise. This highlights the role of the materials in ensuring the modern heat exchanger technologies and also in providing long-term operational effectiveness.
Stainless Steel Tubing Coil Applications
Stainless steel tubing coils are widely accepted across several industries due to their excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and good thermal conductivity. Recent analyzed data reveals diverse applications:
| Industry | Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Processing | Transfer of corrosive or high-temperature fluids | Safety and operational efficiency |
| HVAC Systems | Accurate heat transfer | Reduced power consumption |
| Medical Field | Catheter manufacturing and fluid management | Biocompatibility and reliability |
| Renewable Energy | Solar water heating and geothermal units | Enhanced sustainability |
The varied utilization reflects their necessity in diverse critical applications, combining durability with engineering flexibility to satisfy modern efficiency standards.
Slit Coil and Strip Variants

What is a Slit Coil?
A slit coil is an intricately processed metal coil that is sliced accurately and precisely into strips of specific width, making it suitable for various industrial uses. Slit coils, usually made from stainless steel, aluminum, or carbon steel, retain the original coil’s physical properties while adapting to customer requirements according to precise dimensional tolerances.
Slitting Process:
- Unwinding of the master metal roll
- Cutting into desired sizes using rotary knives
- Winding of strips into individual rolls
- Quality inspection for dimensional accuracy
The industries automotive, construction, electronics, and manufacturing consume slit coils mainly owing to these coils’ strength and versatility. Their being highly precise makes them fit for use in such applications as electrical parts, piping, and transformers where high accuracy and speed are demanded. Continuous advancements in slitting technology keep improving the edge quality and dimensional accuracy that help slit coils stay modern and in line with industry needs.
304 Stainless Steel Strip Characteristics
304 stainless steel strip is the most preferred material in a range of industrial and commercial applications owing to its amazing properties such as resistance to corrosion, durability, and versatility. The alloy mainly consists of iron, chromium (18%), and nickel (8%) which make it non-magnetic, because of its austenitic stainless steel nature.
✓ Strip Characteristics
- High Tensile Strength: Maintains structural integrity under stress
- Excellent Plasticity: Can be worked through deep drawing or bending without losing integrity
- Oxidation Resistance: Withstands harsh environments including acidic and chlorinated conditions
- PreciseDimensions: Manufactured to exact specifications per ASTM A240 standards
- Multiple Finishes: Available in various surface finishes including 2B
Recent advancements in the stainless steel industry have made it possible to produce 304 strips in very exact dimensions and surface finishes according to various industry standards like ASTM A240. This has made it a must-have material in automotive, food processing, medical equipment, and architecture sectors.
Advantages of Different Coil Types
Coils come from materials like stainless steel, aluminum, and copper, each of which has a certain industrial application. The selection of coil type is influenced by the properties of strength, flexibility, corrosion resistance, and conductivity among others.
| Coil Type | Key Properties | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel Coils | Outstanding corrosion resistance, maintains strength under demanding conditions | Energy, construction, medical sectors; exposure to moisture, chemicals, or extreme temperatures |
| Aluminum Coils | Lightweight, high thermal/electrical conductivity, recyclable | Aerospace, automotive, HVAC; heat exchangers and electrical wiring |
| Copper Coils | Superior electrical/thermal conductivity, ductility, oxidation resistance | Electrical engineering, heat transfer systems, power generation, refrigeration |
| Galvanized Coils | Zinc coating provides strong barrier against rust and wear | Roofing, structural support, ventilation systems |
Choosing the right coil type for an application allows industries to optimize performance, lower maintenance costs, and comply with sustainability targets.
Economic Benefits of Using 304 Stainless Steel

Cost Efficiency in Manufacturing
The use of 304 stainless steel in manufacturing is highly cost-effective due to its long lifecycle, corrosion resistance, and minimal maintenance requirements. Although it costs more than alternative materials upfront, its durability limits replacement frequency and repair expenses, creating economically efficient operational budgets.
Cost-Effectiveness Factors:
- Reduced replacement frequency due to durability
- Lower repair and maintenance costs over lifetime
- Efficient operational budgeting
- Environmentally sustainable production practices
- Excellent performance-to-cost ratio
Recent studies reveal that producers who place eco-friendly items on the top of their list still rely on stainless steel mainly due to its good performance along with being economically advantageous. The steady rise in the number of searches for “advantages of 304 stainless steel” and “materials for manufacturing that resist corrosion” supports this fact. The trend implies that the impact on the environment is lessened and at the same time, cost-effective production methods are in place, thus allowing stainless steel to take the center stage.
Long-Term Value and Durability
The primary reason for stainless steel being valued so highly long-term is its remarkable resistance to corrosion, oxidation, and wear, which allows it to last even in the most unfriendly environments. Its combination of high tensile strength and low maintenance demand creates very low lifecycle costs, making it widely accepted across many industrial sectors such as construction, automotive, and food processing.
✓ Corrosion Resistance
Withstands harsh environments without degradation
✓ Low Maintenance
Minimal upkeep requirements reduce operational costs
✓ High Tensile Strength
Maintains structural integrity under stress
✓ Recyclability
Environmentally sustainable material choice
Data from recent analyses indicate that during the last five years, there has been a noticeable increase in search queries for the phrases “long-lasting materials for industrial use” and “stainless steel cost-benefit analysis”. Moreover, it has become apparent that the economic and practical advantages of 304 stainless steel as a durable material have been recognized more widely. The durability and reusability of 304 stainless steel are frequently highlighted as the major reasons supporting its selection that are in line with the industry’s transition to sustainable and cost-efficient manufacturing processes.
Impact on Supply Chain Management
The nexus of increasing demand for robust materials along with rising interest in “stainless steel cost-benefit analysis” denotes very significant supply chain management impacts. This points at a change where the industry is now moving towards materials that are not only strong but also environmentally friendly. Thus, the supply chain has to rethink its strategy, that is, make sure that 304-grade stainless steel is readily available, so that the quality expectations of the market- which is moving ahead- are met.
Supply Chain Considerations:
- Enhanced Collaboration: Manufacturers and suppliers must work closely to ease procurement
- Reliable Sourcing: Ensure dependable raw material sources
- Network Strengthening: Avoid potential bottlenecks through robust supplier networks
- Sustainable Focus: Gradual shift toward environmentally-friendly materials
- Uninterrupted Production: Critical step to keep production cycles flowing and meet consumer requirements efficiently
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
❓ What are the main characteristics of 304 stainless steel coil?
One of the main features of 304 stainless steel coil is its superb anti-corrosion property which is mostly caused by nickel and chromium presence. The alloy steel is also the most chosen material for the food and beverage sector and other industries. The product is usually non-magnetic but sometimes slight magnetism is acquired after cold working or hardening. The alloy steel is welded without difficulty and the surface can be made to have either smooth, 2B, or finer finishes which is to conform with application requirements for aesthetic or hygienic purposes. Carbon content is strictly controlled to prevent carbide precipitation during the welding of the alloy. The 304L variant that contains ultra-low carbon is used where carbide formation has to be minimized. The usual mechanical properties are moderate tensile strength and very good ductility which is the reason why the material is used in a variety of applications.
❓ How does the specification of type 304 metal coil compare with 304L and 316L?
The difference between type 304 and 304L lies primarily in carbon content, with 304L having lower carbon content as a means to counteract carbide precipitation in high-temperature welding. On the contrary, 316L, with its additional molybdenum, has better resistance to pitting and thus, taking into account the harsher environments, it is the one to be chosen over 304 or 304L. The fabricators consider a mix of factors such as welding and corrosion resistance, and of course, price, when they have to select among these grades. In critical applications, it is common to resort to third-party testing to verify the results of chemical analysis and the properties of the materials. In cases of food and beverage applications, or wort chillers and valves, the choice will be 304L or 316L due to the former having lower carbon content and the latter superior corrosion performance.
❓ Can coil stock be slit to width for my fabrication purposes?
Yes, strip coil and slit coil services are standard, and stainless steel coil can be slit to width corresponding to outer diameter and width specifications for subsequent processes. Coil stock is offered in various finishes (like 2B) and different thicknesses according to mechanization properties for specific applications. Slitting reduces material waste and facilitates handling for fabricators producing parts such as valves, tubing, or textile components. Many suppliers stock standard sizes and can perform additional cold working to obtain desired tolerances and work hardening. Always ensure that edges from slitting are burr-free and conform to your polish or finish specifications.
❓ Is 304 stainless steel coil magnetic after processing and cold working?
304 is commonly regarded as non-magnetic in the annealed state. However, cold working, bending, and extensive work hardening can cause a slight magnetic response to develop, so depending on deformation extent, it may become slightly magnetic. This characteristic is crucial for applications depending entirely on non-magnetic properties like some textile or electronic components. For requirements very strict on non-magnetism, alternative alloys or extra low-carbon grades can be specified and verified through third-party testing. When selecting material for magnetic property-sensitive components like wort chillers or medical devices, designers should consider this characteristic.
❓ What surface finishes and thickness options are available for stainless steel tubing coil?
Different surface finishes are provided for stainless steel tubing coil and strip coil, as they are the manufacturer’s main products, with their corresponding aesthetic and functional suppliers like 2B, mirror polishing, and bead blasting. Different thicknesses are used for different applications from very thin ones in cans and food equipment to very thick ones requiring high strength for structural components. Customization is offered for the outer diameter and coil weight, different methods are available for splitting and forming in valves, tubing, or heat exchanger components. Cold working and annealing are the production steps that determine mechanical properties and work hardening characteristics, thus production routes are balancing strength and formability. Many suppliers maintain inventory of commonly requested sizes for quick delivery along with custom runs for special projects.
❓ How should I consider welding, corrosion resistance, and long-term performance for 304 coil in food and beverage applications?
304 steel has rather good resistance to corrosion in most of the food and beverage processing situations, and it also gives a great possibility of 304 joint welding for such applications as tanks, wort chillers, and valves. Considering that the welding joints will be in places where there are high temperatures or chloride environments, it is wise to use 304L (extra low carbon) because carbide precipitation and intergranular corrosion cannot occur in the heat-affected zone around welds. 316L is the drainage of pitting resistance due to its molybdenum content and superior alloy performance, when even higher pitting resistance is required. Together, regular inspection and appropriate surface treatment like polishing or passivation can prolong the material’s lifespan in different applications. In case it is needed, consulting material properties and certification via third-party testing is advisable as a method of compliance with hygiene and safety standards.